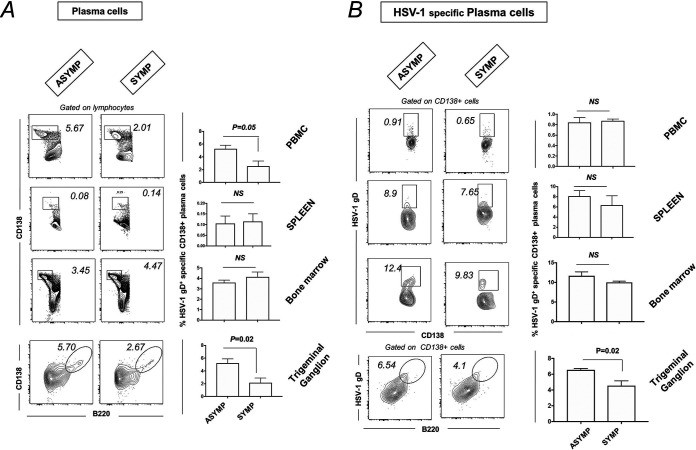
FIG 5.
Plasma cell profile in PBMC, spleen, bone marrow, and TG of ASYMP and SYMP HSV-1-infected mice. For this experiment, the corneas of B6 mice (n = 6) were infected with HSV-1 McKrae (1 × 106 PFU/eye) by scarification, and virus reactivation was provoked at day 35 p.i. in latently infected mice using 60 s corneal UV-B irradiation. At day 6 postreactivation, mice were categorized into ASYMP or SYMP depending on disease occurrence. ASYMP and SYMP mice were euthanized, and immune cells from peripheral blood, spleen, and bone marrow were collected for flow cytometry staining for plasma cells. (A) Representative plots for plasma B cells (CD138+ B cells) in PBMC, spleen, BM, and TG (Right) of ASYMP and SYMP mice is shown. Graph showing percentage of plasma B cells (CD138+ B cells) in PBMC, spleen, PBMC, and TG (Right) of ASYMP and SYMP mice. (B) Representative FACS plot showing HSV-1-specific plasma B cells (HSV-1 gD+CD138+ B cells) in PBMC, spleen, PBMC, and TG (Left) of ASYMP and SYMP mice. Graph showing percentage of HSV-1-specific plasma B cells (HSV-1 gD+CD138+ B cells) in PBMC, spleen, PBMC, and TG (Right) of ASYMP and SYMP mice.