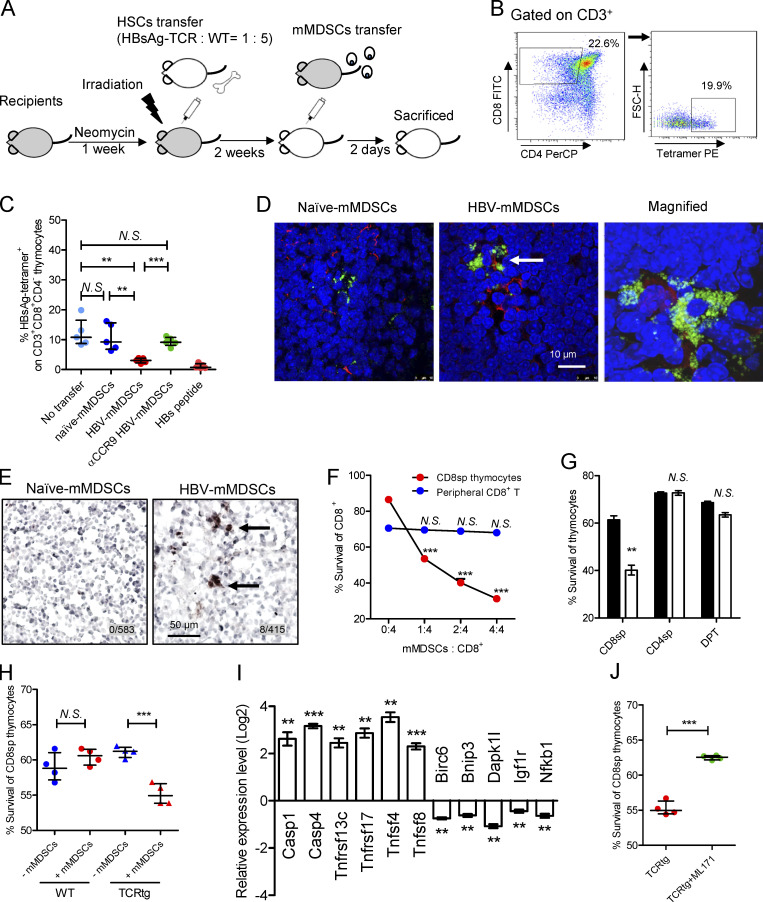
Figure 5.
mMDSCs promote death of HBsAg-specific CD8+ thymocytes. (A) Experimental steps for immune reconstitution and adoptive transfer of mMDSCs. (B) Gating strategy for HBsAg-specific CD8+ thymocytes. (C) Detecting HBsAg-specific CD8+ thymocytes via flow cytometry in reconstituted mice on day 3 after transfer of mMDSCs (107 cells per mice, n = 5). (D) IF detection of colocalization of mMDSCs (Gr1, green) and HBsAg-specific CD8+ thymocytes (MHC-I tetramer, red) at 36 h after transfer of mMDSCs, triplicate. Arrows indicate the positive signaling in the IF detection. (E) Detecting cleaved caspase-3 in thymi of mice at 36 h after transfer of mMDSCs (brown, 400X), triplicate. Arrows indicate the positive signaling in the IHC staining. (F) Coculture of HBV-persistent HDI mice–derived mMDSCs (effector, E) with CD8+CD4− (CD8sp) thymocytes or peripheral CD8+ T cells (target, T) from HBsAg-TCR transgenic mice for 18 h. Detection of Annexin V and 7-ADD double negative cells (n = 5). (G) Coculture of naive (empty) mice– or HBV-persistent HDI (filled) mice–derived mMDSCs with HBsAg-TCRtg thymocytes (E: T = 1: 2; n = 4). (H) Coculture of HBV-persistent HDI mice–derived mMDSCs with thymocytes from WT or HBsAg-TCRtg mice (E: T = 1: 2; n = 4). (I) Levels of genes related to cell death in HBsAg-TCRtg CD8+CD4− thymocytes after coculture with HBV-persistent HDI mice–derived mMDSCs (5 h). (J) Coculture of HBV-persistent HDI mice–derived mMDSCs with TCRtg CD8+CD4− thymocytes in the presence of 5 μM NOX1 inhibitor (ML171). **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.