Figure 1.
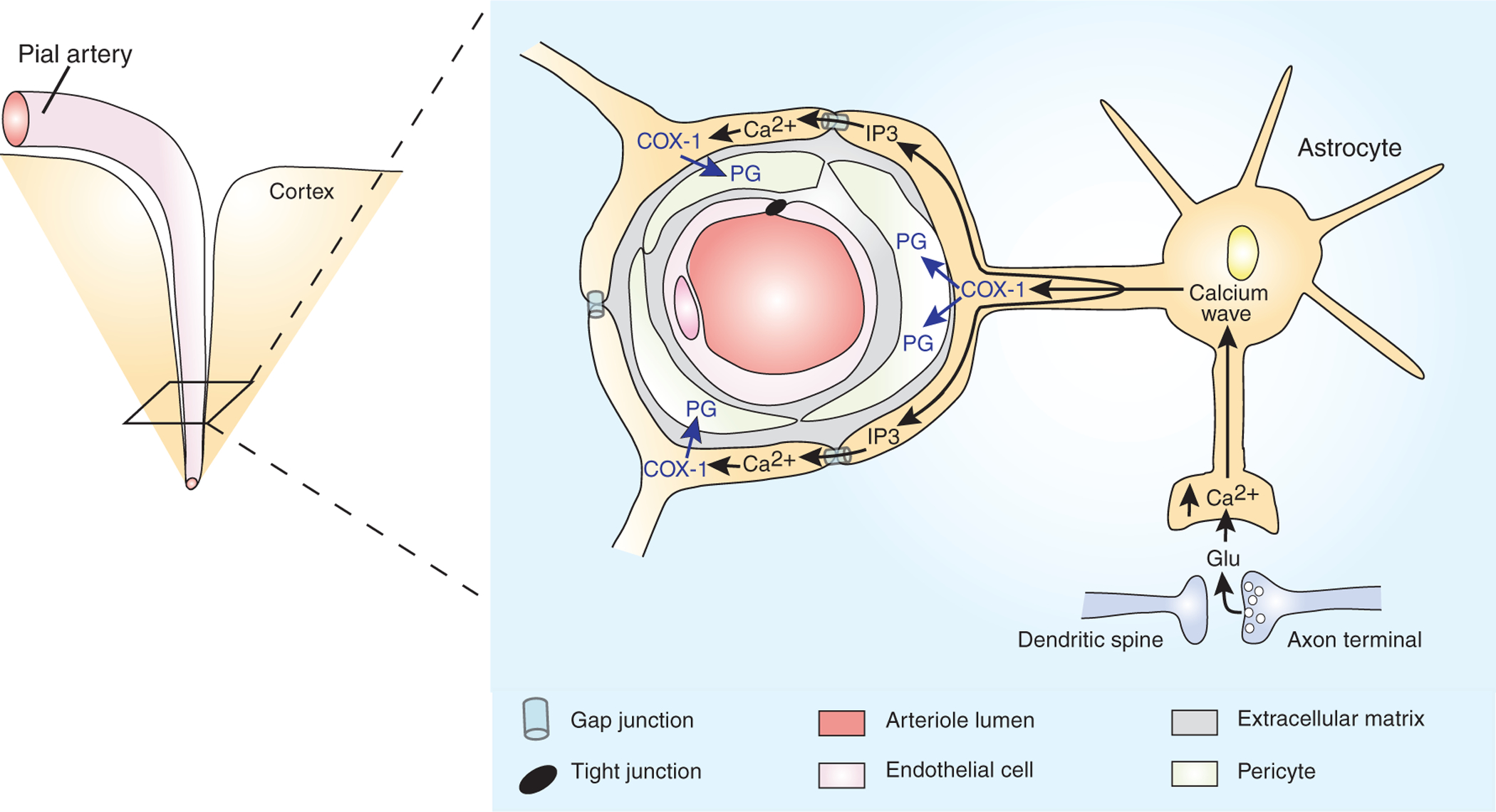
Astrocytes couple increased local blood flow to neuronal activity. By sending specialized processes both to arterioles (astrocyte endfeet) and to glutamatergic synapses, cortical astrocytes form an anatomical link between neurons and the blood supply. During neuronal activity, glutamate spills out of glutamatergic synapses, and, by activating astrocytic metabotropic glutamate receptors, triggers an astrocytic calcium wave. As the calcium wave invades an astrocytic endfoot, Ca2+ stimulates phospholipase A2 to produce arachidonic acid (AA). The AA is metabolized by the cyclooxygenase, COX-1, into a vasodilating prostaglandin (PG). Coordinated vasodilation is facilitated by Ca2+-induced production of IP3, which passes through gap junctions to trigger synchronous calcium waves and PG production in neighboring endfeet. For simplicity, PG is depicted as inducing vasodilation by acting in pericytes that surround the arteriole4. However, the site of action of PG is unknown, and there are other arteriole-associated cell types.
