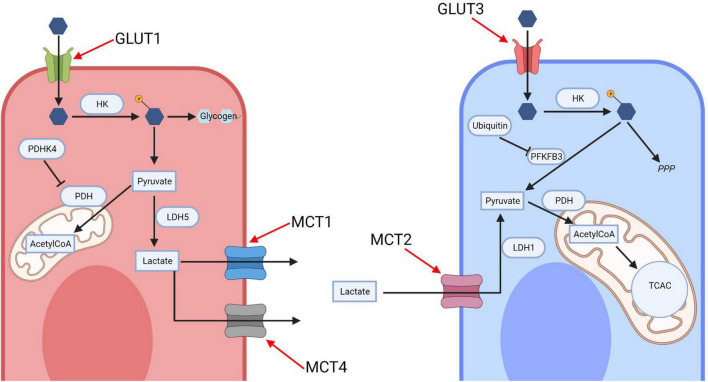
FIGURE 1.
The astrocyte-neuron lactate shuttle (ANLS). Glucose is imported into neurons and astrocytes by their respective transporters, GLUT1 and GLUT3, before being phosphorylated by hexokinase. In neurons most glucose-phosphate is subsequently metabolized along the pentose phosphate pathway, with the early glycolytic enzyme PFKFB3 being inhibited by ubiquitin action. In astrocytes glucose-phosphate is converted into glycogen for storage or metabolized via glycolysis to produce pyruvate, which either enters the mitochondria or is converted into lactate by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) 5. Lactate is exported by the monocarboxylate transporters (MCT) 1 and 4 and imported into neurons via the MCT 2. It is then converted back to pyruvate via LDH-1 and enters the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation cycle. HK, hexokinase; PDHK4, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; MCT, monocarboxylate transporter; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; TCAC, tricarboxylic acid cycle; PFKFB3, 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3; PPP, pentose phosphate pathway; AcetylCoA, Acetyl coenzyme A. Created with: BioRender.com.