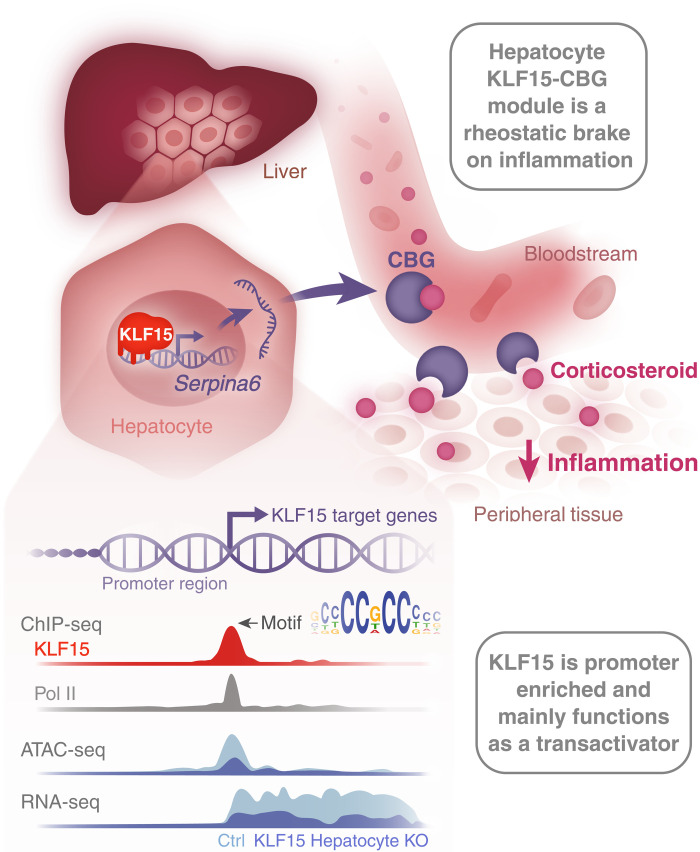
Fig. 5. Summary diagram.
In hepatocytes, the zinc finger transcription factor KLF15 directly binds the Seprina6 proximal promoter and transactivates Serpina6 mRNA expression, leading to the synthesis of CBG protein. CBG is abundantly secreted by hepatocytes into the bloodstream, where it regulates free versus total corticosteroid hormone concentration and dynamically releases bound corticosteroids at sites of inflammation as a mechanism to rheostatically suppress local inflammatory activation. Deletion of Klf15 in mouse hepatocytes in vivo leads to profound reduction of plasma CBG concentration, decreased plasma corticosterone binding capacity, and increased mortality during acute inflammatory challenge. These phenotypes are completely rescued by reconstituting CBG expression in the livers and plasma of Klf15-deficient mice in vivo. Using the newly generated Klf153xFLAG mouse strain described in this study, ChIP-seq for endogenous KLF15 was performed in adult mouse liver tissue and integrated with RNA-seq and ATAC-seq from liver tissue of mice deficient versus sufficient in hepatocyte KLF15. In the liver, KLF15 was found to be predominantly enriched at gene promoters, where it binds a palidromic GC-rich consensus element, maintains open chromatin, and transactivates proximal target genes.