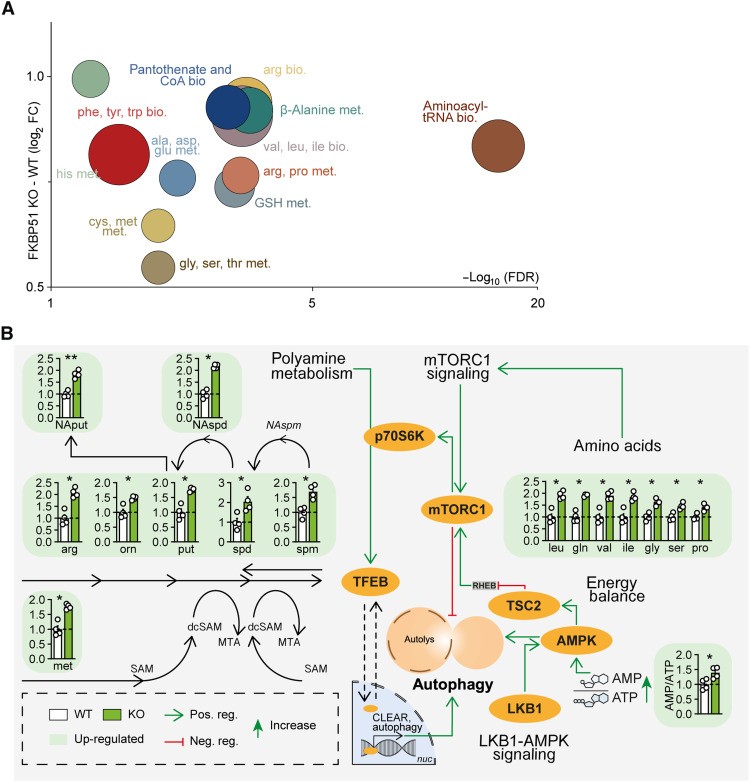
Fig. 1. FKBP51 associates with amino acids and polyamine biosynthesis pathways.
(A) Analysis and regulation of significantly altered pathways of FKBP51 KO and WT cells. The f(x) axis shows the (median) log2 fold change (FC) of all significantly altered metabolites of the indicated pathway, and the false discovery rate (FDR) (equals the −log10–adjusted P value) is shown on the x axis. The size of the circles represents the amount of significantly changed metabolites in comparison to all metabolites of a particular pathway. tRNA, transfer RNA. (B) FKBP51 deletion increases metabolites of the polyamine pathway, the AMP/ATP ratio, and enhances levels of amino acids associated with mTOR signaling. Data in (B) are shown as means + SEM and were analyzed by a two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and a subsequent Bonferroni multiple comparison analysis. ala, alanine; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; arg, arginine; asp, asparagine; bio., biosynthesis; CoA, coenzyme A; cys, cysteine; dcSAM, decarboxylated S-adenosylmethione; gln, glutamine; glu, glutamic acid; gly, glycine; GSH, glutathione (reduced); his, histidine; ile, isoleucine; leu, leucine; LKB1, liver kinase B1; met, methionine; met., metabolism; MTA, 5′-methylthioadenosine; mTORC1, mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1; NAput, N-acetylputrescine; NAspd, N-acetylspermidine; NAspm, N- acetylspermine; orn, ornithine pro, proline; phe, phenylalanine; put, putrescine; SAM, S- adenosylmethionine; ser, serine; spd, spermidine; spm, spermine; TFEB, transcription factor EB; TSC2, tuberous sclerosis complex 2; thr, threonine; trp, tryptophan; tyr, tyrosine; val, valine. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.