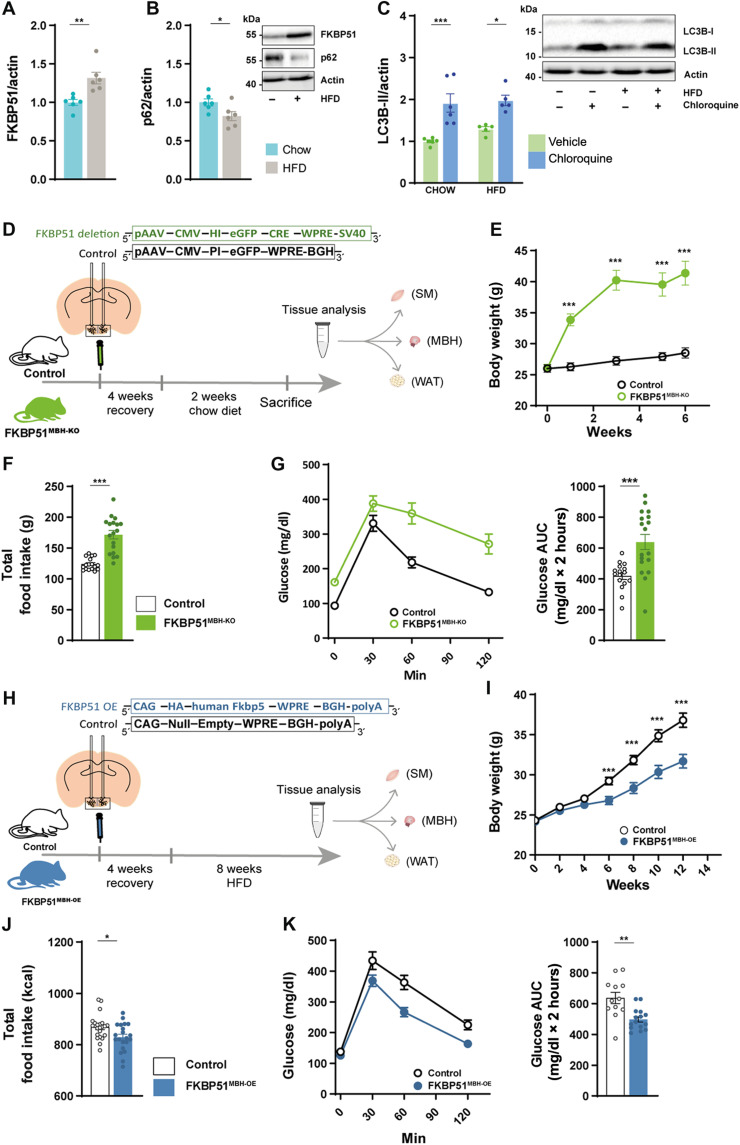
Fig. 4. MBH FKBP51 regulates body weight gain, food intake and glucose metabolism.
(A) Ten weeks of HFD increased hypothalamic FKBP51 in the MBH [n (chow) = 6 versus n (HFD) = 6]. (B) Effects of HFD on the accumulation of p62. (C) Treatment with chloroquine (50 mg/kg) increased LC3B-II level under chow and HFD conditions. (D) FKBP51lox/lox animals were injected with 200 nl of Cre-expressing virus and fed a chow diet for 6 weeks. (E) FKBP51MBH-KO showed significant body weight increase after virus injection on a regular chow diet. (F) FKBP51MBH-KO animals showed increased food intake and (G) enhanced glucose intolerance. AUC, area under the curve. (H) For FKBP51 overexpression, animals were injected with an AAV virus into the MBH. (I) FKBP51MBH-OE animals showed reduced body weight gain on an HFD diet compared to their control animals (J) FKBP51MBH-OE animals showed reduced food intake. (K) FKBP51MBH-OE animals showed improve glucose tolerance under HFD conditions. For (A), (B), (F), (G), (J), and (K), an unpaired Student’s t test was performed. For (C), a two-way ANOVA was performed, followed by a Tukey’s multiple comparison test. For (E) and (I), a repeated measurements ANOVA was performed. ± SEM; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.