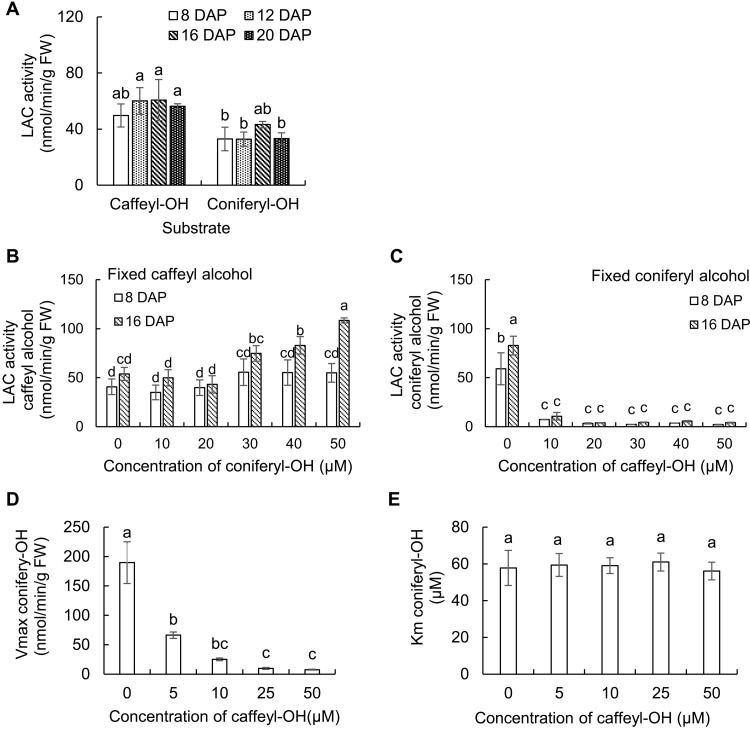
Fig. 7. Laccase activities in the C. hassleriana seed coat.
(A) Laccase activity against caffeyl and coniferyl alcohols in protein extracts from Cleome seed coat cell walls during different developmental stages. Activity was calculated by substrate disappearance monitored by HPLC. Identification of reaction products is provided in Fig. 6 and figs. S8 and S9. (B and C) Effects of coniferyl alcohol on the oxidation of caffeyl alcohol, and vice versa, in cell wall protein extracts from Cleome seed coats at 8 and 16 DAP. Increasing concentrations of one monolignol were added, while the concentration of the other was maintained at 50 μM. (D and E) Kinetic properties of laccases in cell wall protein extracts from Cleome seed coats at 16 DAP against coniferyl alcohol in the presence of caffeyl alcohol. Protein extracts were incubated with 25 to 200 μM coniferyl alcohol and 0 to 50 μM caffeyl alcohol, and kinetic constants were calculated and plotted. Laccase activities were measured in the presence of catalase to inhibit peroxidase as described in Materials and Methods. Approximately 300 mg of seed coats isolated from seeds harvested from each individual Cleome plant were counted as one biological replicate. Data are means ± SE derived from three biological replicates. The different letters above the bars represent statistically significant differences determined by analysis of variance (ANOVA) (Duncan, P ≤ 0.05) with SPSS Statistics (version 27; IBM) FW, fresh weight.