FIGURE 5.
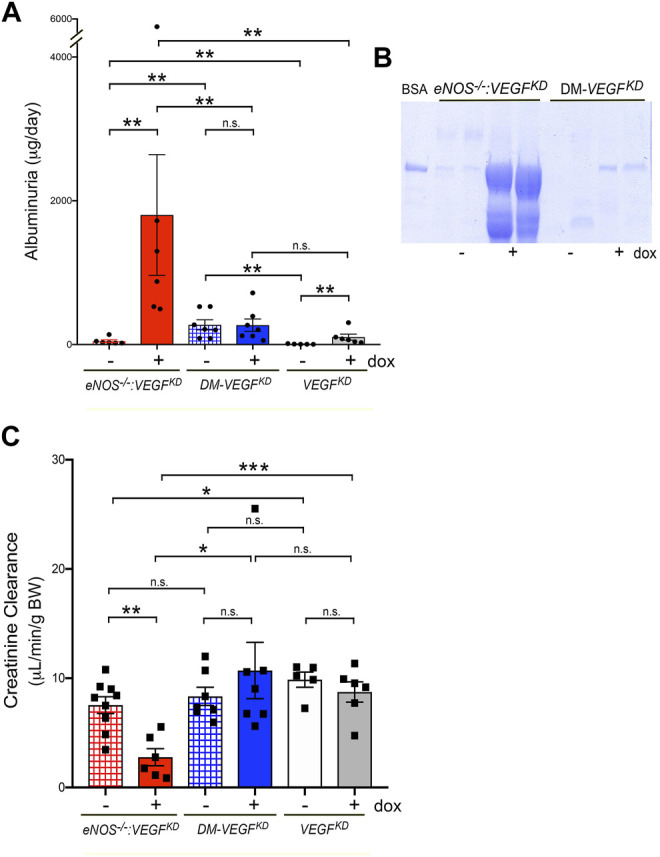
Podocyte VEGFKD causes massive proteinuria and renal failure in eNOS−/−:VEGFKD mice. (A) Induction of VEGFKD in eNOS−/−:VEGFKD (+dox) mice (red bar) increases albuminuria ∼30 fold higher than in control eNOS−/−:VEGFKD (− dox) (**, p = 0.0022) but does not change albuminuria in diabetic mice (DM-VEGFKD + dox, blue bar) (n.s., p = 0.9015); VEGFKD causes mild albuminuria in non-diabetic mice (VEGFKD + dox, gray bar) compared to controls (VEGFKD − dox, white bar) (**, p = 0.0043), Mann-Whitney test. (B) SDS PAGE/Coomassie stain shows severe albuminuria in eNOS−/−:VEGFKD + dox and milder albuminuria in diabetic VEGFKD + dox mice; BSA = bovine serum albumin marker, urine volume loading was normalized to creatinine. (C) Creatinine clearance decreases upon VEGFKD induction in eNOS−/−:VEGFKD + dox mice (red bar) to ∼1/3 of control eNOS−/−:VEGFKD − dox (***, p = 0.0009), but is not significantly altered in diabetic mice (DM-VEGFKD − dox and + dox, hatched/blue bars) (n.s., p = 0.4114) or VEGFKD in non-diabetic mice (VEGFKD − dox and + dox, white/gray bars) (n.s., p = 0.359) with intact eNOS; induced eNOS−/−:VEGFKD (+dox) mice had significantly lower Creat Cl than diabetic VEGFKD + dox and non-diabetic VEGFKD + dox mice (*, p = 0.02 and ***, p = 0.0007, respectively).
