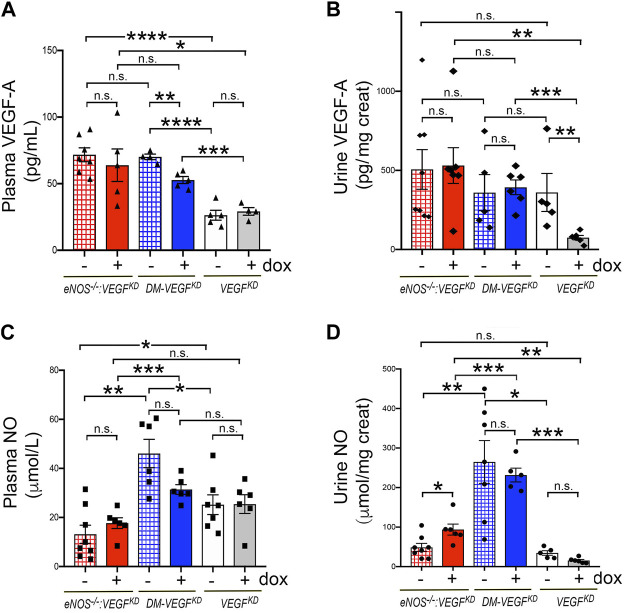
FIGURE 6.
Effect of VEGFKD on circulating and urine VEGF-A and NO in diabetic and eNOS−/−:VEGFKD mice. (A) plasma VEGF-A is similarly elevated in eNOS−/−:VEGFKD mice (red bars) irrespectively of VEGFKD , as compared to non-diabetic eNOS intact mice (VEGFKD − dox, white bar) (****, p =<0.0001) or VEGFKD + dox mice (gray bar) (*, p < 0.005); in diabetic mice VEGFKD (DM-VEGFKD + dox, blue bar) significantly decreases circulating VEGF-A (**, p = 0.0013), but all diabetic mice have plasma VEGF-A >2-fold higher than non-diabetic mice with intact eNOS (VEGFKD , white/gray bars) (****, p < 0.0001 and ***, p = 0.0006). (B) Urine VEGF-A: podocyte VEGFKD does not alter VEGF-A excretion in eNOS−/−:VEGFKD (red bars) or diabetic mice (blue bars); VEGFKD significantly inhibits VEGF-A excretion in non-diabetic mice (VEGFKD + dox, gray bar) (**, p = 0.0043). (C) Plasma NO: podocyte VEGFKD (+ dox) does not significantly alter plasma NO in any experimental group; plasma NO is lower in eNOS−/−:VEGFKD (red bars) than diabetic (blue bars) (**, p = 0.001 and ***, p = 0.0009) and non-diabetic mice with intact eNOS (white bar) (*, p = 0.047); plasma NO is higher in diabetic (DM-VEGFKD − dox, hatched blue bar) than in non-diabetic mice (VEGFKD − dox, white bar) (*, p = 0.015) and VEGFKD abrogates this change (DM-VEGFKD + dox, blue bar). (D) Urine NO: VEGFKD increases NO excretion in eNOS−/−:VEGFKD + dox mice (*, p = 0.0272, red bar); all diabetic mice (blue bars) have several fold higher NO excretion than non-diabetic mice (white/gray bars), irrespectively of VEGFKD .