Figure 2.
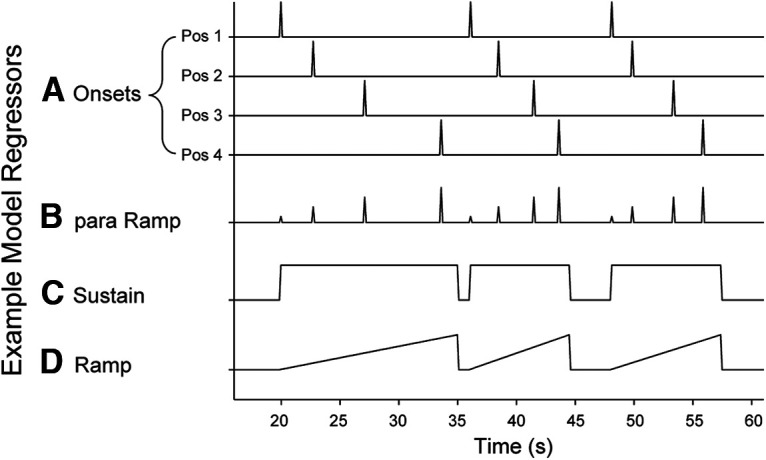
Example model regressors. A, Onsets were modeled separately for each position as instantaneous (zero duration) events corresponding to the sequence position onsets model (Model 1; see Materials and Methods). B, Parametric ramp regressors were used for the parametric sequence position (ramping) model. Linear increase across positions 1–4 with instantaneous onsets (Model 2). C, Sustain regressors were constructed as a square wave from the onset of position 1 to the offset (response) of position 4 (models 3 and 4). D, Ramp regressors linearly increased from the onset of the position 1 to the offset of position 4 (Models 3 and 4). All regressors shown were separated by visibility and reward conditions (e.g., a model containing onsets would contain 16 regressors: Occluded High positions 1–4; Occluded Low positions 1–4; Visible High positions 1–4; Visible Low positions 1–4). s = seconds. Figure adapted from Desrochers et al. (2015).
