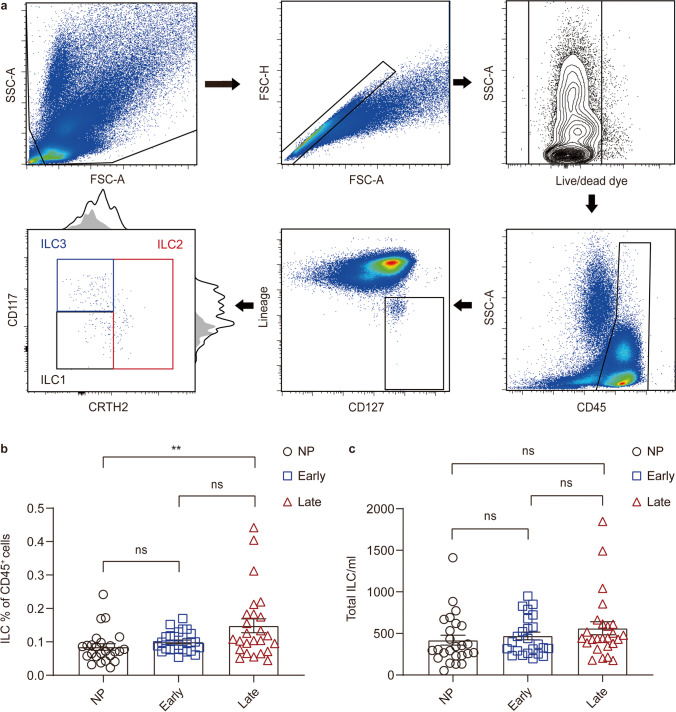
Fig. 1.
Late pregnancy displays the highest circulating ILC proportion in human peripheral blood. a Flow cytometry gating strategies for the identification of peripheral blood ILC subsets. ILCs are defined as CD45+Lin− (including CD3ε, CD4, CD5, CD14, CD19, CD56, CD11c, CD11b, CD34, CD123, TCRɑβ, TCRγδ, and FcεRIɑ) CD127+ cells. The distribution of ILC1 (CD117−CRTH2−; black), ILC2 (CRTH2+; red) and ILC3s (CD117+CRTH2−; blue) were determined. Histograms represent expression analysis with the FMO as grey area and the stained sample as line. Comparison of circulating ILC percentage in CD45+ cells (b) and absolute counts (c) in non-pregnant, early-pregnant, and late-pregnant women. NP, non-pregnant women. Data are shown as means ± SEMs and were analyzed by Kruskal-Wallis tests. Each point indicates an individual. **P < 0.01. ns, not significant