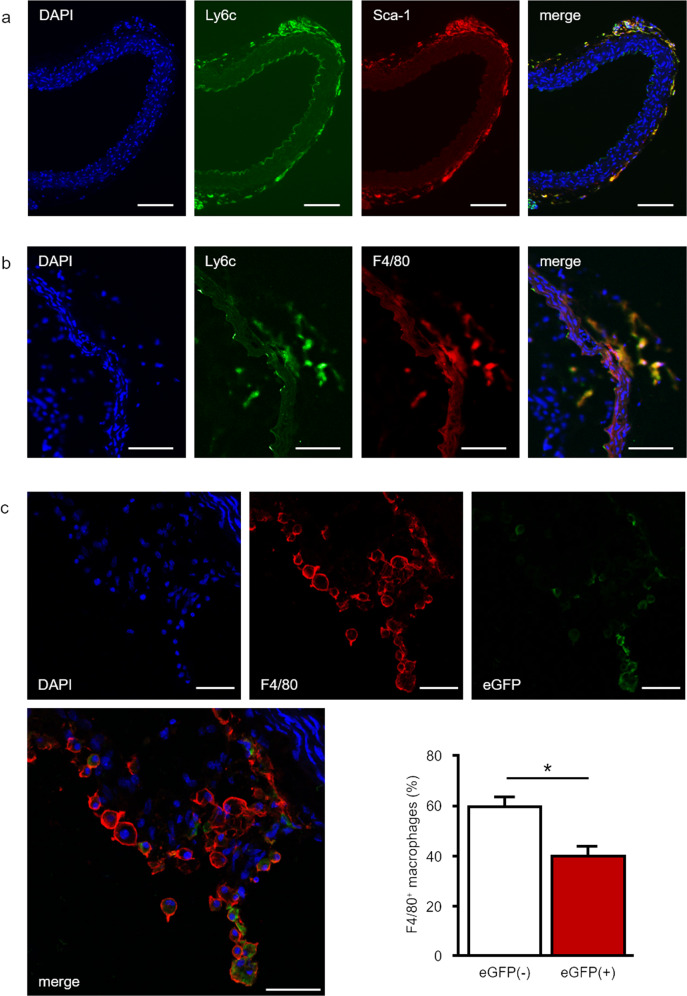
Fig. 2. The majority of macrophages in ARA originates from bone marrow-independent progenitors.
a Cross-sections of freshly isolated murine aortae were analyzed by immunofluorescence for the presence of Ly6c+ and Sca-1+ progenitor cells. Within the adventitia, a substantial part of Ly6c+ cells co-expressed Sca-1 distinguishing them from Ly6c+ monocytes that derived from the bone marrow and circulate in peripheral blood. b After ARA, cross-sections of murine aortae were analyzed by immunofluorescence for the presence of Ly6c+/F4/80+ cells. The majority of F4/80+ macrophages also expressed Ly6c suggesting their derivation from Ly6c+ progenitor cells. c Confocal image of a cross-section of a cultured aortic ring from the FlkSwitch mouse. These sections were screened for F4/80+ cells (red immunofluorescence) and eGFP+ cells (bone marrow-derived). Quantitative analysis of these sections (n = 6) confirmed that 40% of F4/80 macrophages originate from bone marrow-derived cells (F4/80+/eGFP+) whereas 60% are generated from bone marrow-independent progenitors (F4/80+/GFP-). Scale bars: in a, b 100 µm, in c 50 µm.