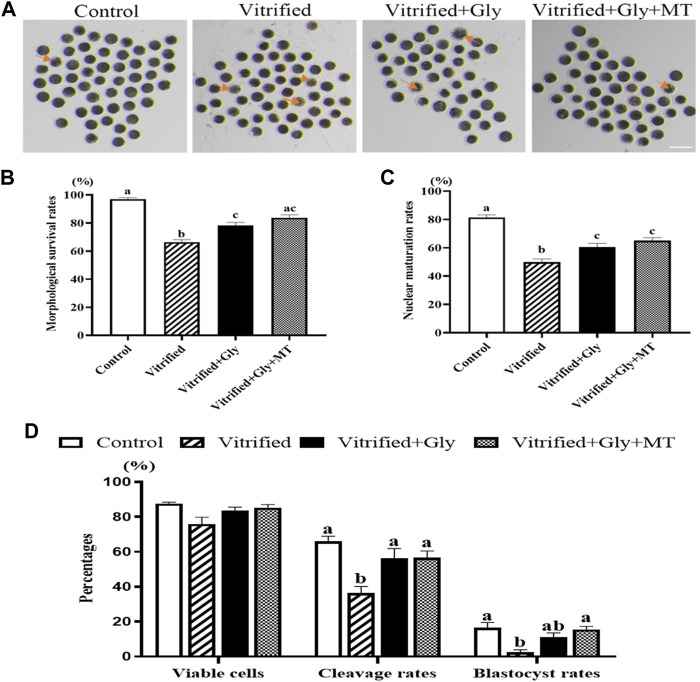
FIGURE 1.
Effects of glycine or glycine plus melatonin supplementation during vitrification, thawing and in vitro maturation on oocyte survival, maturation and subsequent preimplantation development. (A): Representative images of oocytes were collected 44 h after maturation in vitro to determine whether they were alive or not morphologically in each examined group. The arrows indicate dead cells. Scale bar: 200 μm. (B): The survival rates of oocytes collected from each group. (C): The percentages of oocytes with the first polar body (number of MII oocytes/number of survival oocytes) in each experimental group. (D): The rates of alive oocytes (number of morphologically alive oocytes after IVF/total number of oocytes used for fertilization), cleavage (number of cleaved embryos/number of morphologically viable oocytes after IVF) and blastocyst (number of blastocysts/number of viable oocytes) in each examined group. Control: oocytes were neither vitrified/thawed nor supplemented with glycine or melatonin to assist their maturation; Vitrified: oocytes were sequentially vitrified, thawed and cultured for maturation without glycine or melatonin supplementation; Vitrified + Gly: oocytes were sequentially vitrified, thawed and cultured for maturation with glycine supplementation; Vitrified + Gly + MT: oocytes were sequentially vitrified, thawed and cultured for maturation with glycine plus melatonin supplementation. All experiments were performed in triplicate. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Different lowercase letters above columns denote statistical difference at p < 0.05. The same lowercase letters above columns denote that the data are not significantly different at p > 0.05.