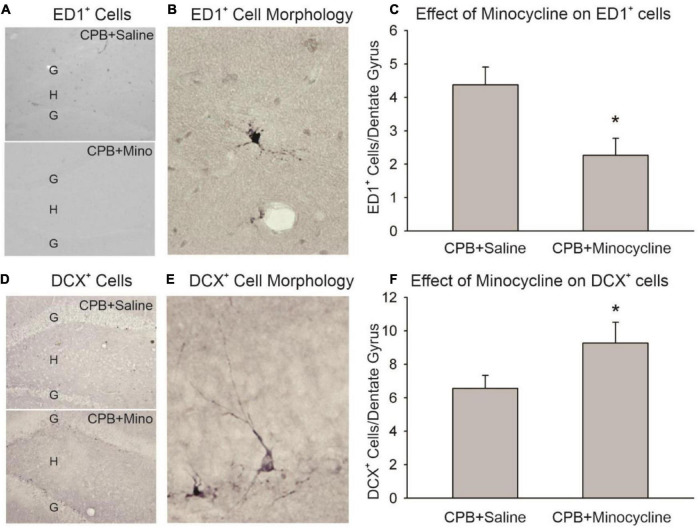
FIGURE 1.
The effect of minocycline on neuroinflammation and neurogenesis. (A) Immunohistochemical staining with ED1 in the dentate gyrus. The granule cell layer (G) and hilus (H) of the dentate gyrus are shown in sections from the CPB + Saline and CPB + Minocycline groups. (B) An example of the morphology of an ED1-positive (ED1+), activated microglia/macrophage in the dentate gyrus. (C) Unbiased cell counting was performed for ED1-positive cells at 6 months post-CPB. There were significantly fewer ED1-positive cells in the CPB + Minocycline group as compared to the CPB + Saline group. Values shown are Means and SEMs (*p < 0.05; t-test). (D) Immunohistochemical staining for DCX in the dentate gyrus in sections from CPB + Saline and CPB + Minocycline groups. (E) An example of the morphology of a DCX-positive (DCX+), immature neuron in the dentate gyrus. (F) Unbiased cell counting was performed for DCX-positive cells at 6 months post-CPB. There were significantly more DCX-positive cells in the CPB + Minocycline group as compared to the CPB + Saline group. Values shown are Means and SEMs (*p < 0.05; t-test).