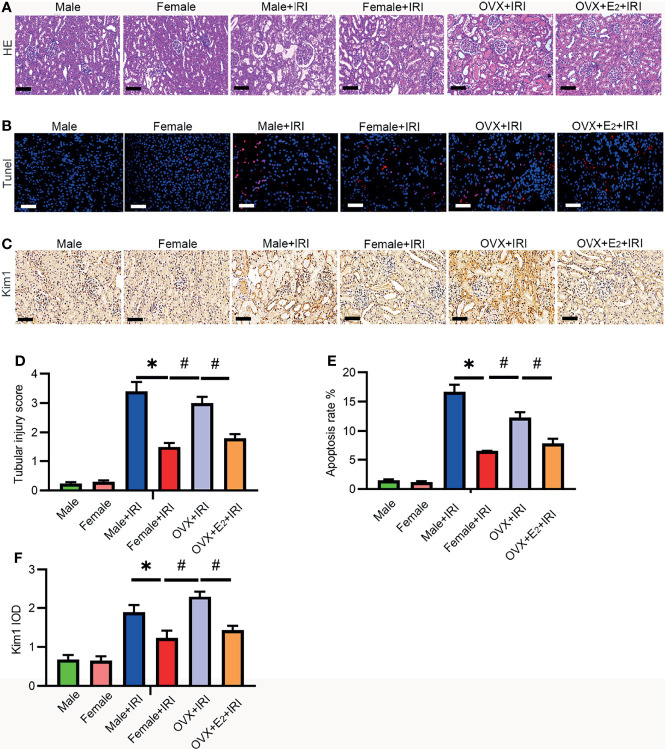
Figure 2.
E2 ameliorated IRI-induced kidney injury. (A) After 45 min of ischemia followed by 24 h of reperfusion, the tubular injury levels in female rat kidneys were examined by HE staining (A) and statistically analyzed (D). One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post-hoc test, * p < 0.05, vs. female+IRI. # p < 0.05, vs. OVX+IRI. Bar = 100 μm. (B) Apoptotic cells in kidney tissues were examined by TUNEL-FITC staining (B) after 45 min of ischemia followed by 24 h of reperfusion and statistical analysis (E). One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post-hoc test, * p < 0.05, vs. female+IRI. # p < 0.05, vs. OVX+IRI. Bar = 100 μm. (C) Kidney injury was examined by IHC with a Kim-1 antibody after 45 min of ischemia followed by 24 h of reperfusion and statistical analysis (F). Bar = 100 μm. One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post-hoc test, * p < 0.05, vs. female+IRI. # p < 0.05, vs. OVX+IRI, n = 6 in each group. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM.