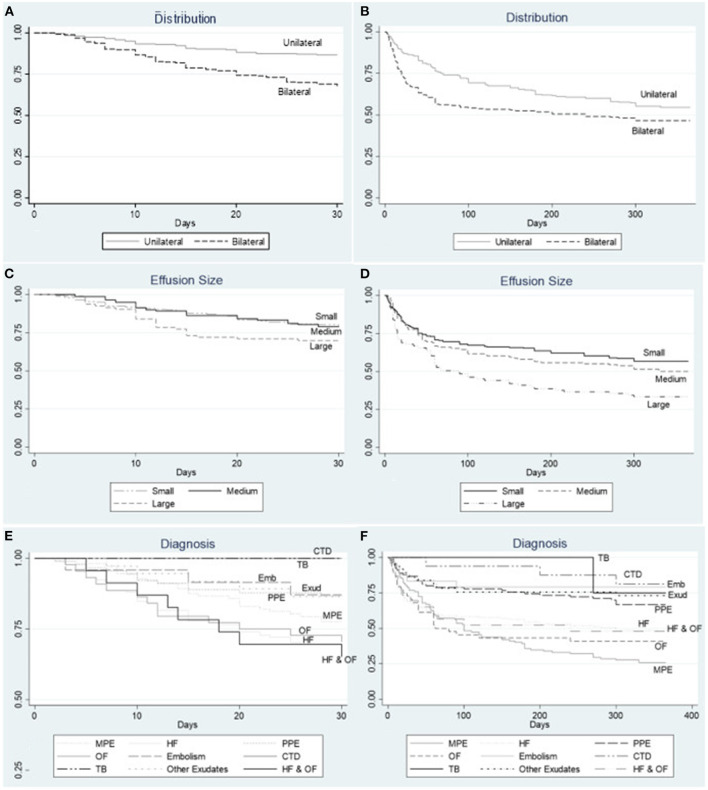
Figure 3.
Kaplan Meier survival curves at 1 month and 1 year by (A,B) distribution of PE. In both time periods, the presence of bilateral pleural effusion was associated with lower survival probability. (C,D) size of PE. In both time periods, the presence of large pleural effusion was associated with lower survival probability. (E,F) diagnosis of PE. Short-term survival is lower for patients with pleural effusions secondary to organ failure (heart, liver, renal) and multiple benign etiologies, while long-term survival is worse for patients with MPE. HF, heart failure; MPE, malignant pleural effusion; PPE, parapneumonic pleural effusion; CTD, connective tissue disease; Emb, pulmonary embolism; OF, organ failure; Exud, other exudate; TB, tuberculosis.