Fig. 3.
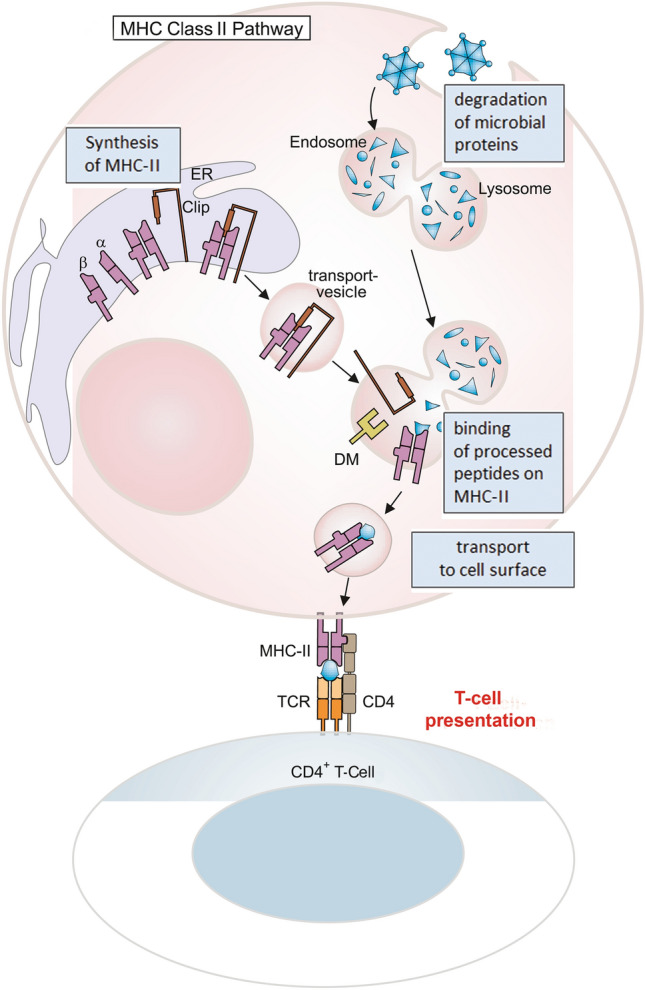
Processing of protein antigens: the MHC-II pathway. Protein antigens are taken up by antigen-presenting cells (APC) into endosomes, which then fuse with lysosomes. There the proteins are broken down into protein fragments. After their synthesis in the ER, MHC-II molecules are transported in vesicles. Newly synthesized MHC-II molecules carry a peptide that occupies the antigen binding site and is called CLIP (class II invariant chain peptide). If both vesicles fuse, CLIP is released from the peptide binding site of the MHC-II by the protein DM and MHC-II can now bind antigen fragments. These MHC-II/peptide complexes are then transported to the cell membrane and can be recognized by CD4-positive cells ([75] with kind permission)
