Figure 7.
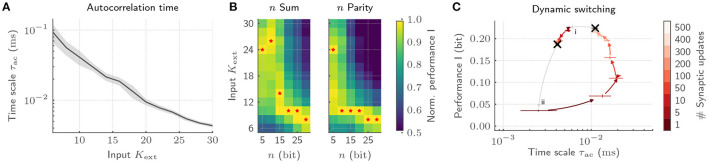
Exploiting collective dynamics for information processing on BrainScaleS-2. (A) The autocorrelation time τac of recurrent SNNs can be controlled by changing the input strength Kext under the constant application of homeostatic regulation. (B) The emerging autocorrelation times for low Kext can be exploited for complex, memory-intensive task processing. Both, a n bit sum as well as a n bit parity task profit from the complex processing capabilities for high n. Low n task, in contrast, profit from short time scales and hence high Kext. The optimal Kext for each n is highlighted by red stars. As a result, each task requires its own dynamic state. (C) The adaptation of the network dynamics to task requirements can be achieved by switching the input strength under the constant action of homeostatic regulation irrespective of the initial condition. Here, the transition from a state with long time scales to short ones is completed with only a few homeostatic weight updates (i). The reverse transition requires a longer relaxation phase (ii).