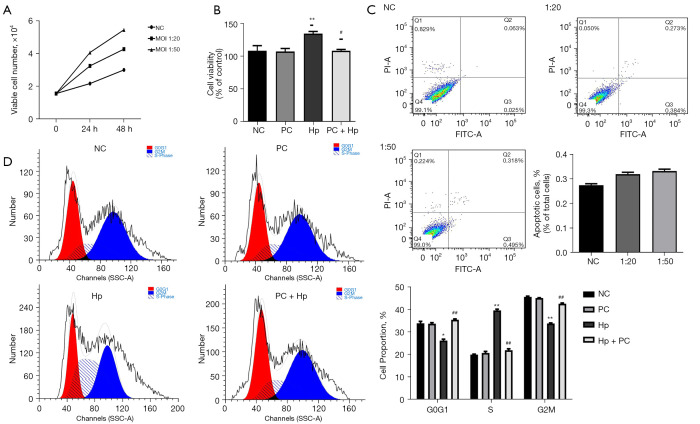
Figure 1.
Effect of phycocyanin on the Hp infection-induced proliferation of AGS cells. (A) AGS cells were infected at a MOI of 1:20 and 1:50, and their cell viability was determined at 24 h and 48 h using the CCK-8 assay. (B) AGS cells were cultured for 24 h with or without Hp infection and with or without the addition of phycocyanin, and the number of viable cells was determined. (C) Analysis of Hp infection-induced apoptosis in AGS cells at 48 h post MOI 1:20 and 1:50 infection. Histograms represent the percentage of apoptotic cells. Apoptotic cells included Annexin V+/PI– and Annexin V+/PI+ cells. (D) Phycocyanin intervention in AGS cells 24 h after exposure to Hp at a MOI of 1:50 for 24 h to assess its effect on AGS cell cycle in each group. Bars represent mean ± standard deviation (**, P<0.01 vs. NC group; *, P<0.05 vs. NC group; ##, P<0.01 vs. Hp group; #, P<0.05 vs. Hp group). NC, AGS cells were not infected with Hp and not treated with phycocyanin; PC, cells were treated with only 150 µM phycocyanin for 24 h; Hp, cells were infected with Hp at a MOI of 1:50 for 24 h; PC + Hp, cells were treated with 150 µM phycocyanin for 24 h post infection with Hp at a MOI of 1:50 for 24 h. Experiments were performed in triplicate for each set of data. MOI, the multiplicity of infection (number of AGS cell: Hp); FITC, fluoresceine isothiocyanate; PI, propidium iodide; CCK-8, Cell Counting Kit-8.