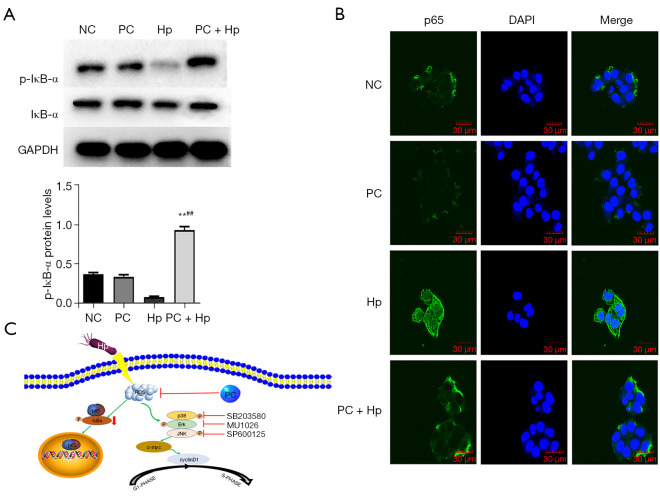
Figure 6.
Effect of phycocyanin on NF-κB signaling pathway activation in Hp-infected AGS cells and Mechanism of action of phycocyanin in Hp infected cells. (A) Western blot assay of whole-cell lysates for the phosphorylation-specific and total form of IκB-α levels in 150 µM phycocyanin-pre-treated AGS cells 24 h post-Hp infection of cells at 50:1 (cells/bacteria) for 12 h (**, P<0.01 vs. NC group; ##, P<0.01 vs. Hp group). (B) Immunofluorescence-based detection of NF-κB p65 in AGS cells post intervention with 150 µM phycocyanin for 24 h followed by infection with Hp for 12 h (cell to Hp ratio of 1:50). Cells were stained with mouse anti-p65 antibody and 488-labeled goat anti-mouse IgG antibody. The left panel shows p65 immunocytochemical staining (green), and DAPI was used to stain the nuclei (blue), scale bar = 30 µm. NC, AGS cells were neither infected with Hp nor treated with phycocyanin; PC, cells were treated with 150 µM phycocyanin only; Hp, cells were infected with Hp at 50:1 (cells/bacteria) for 4 h; PC + Hp, AGS cells were infected with Hp post-24 h intervention with 150 µM phycocyanin. (C) In Hp-infected AGS cells, phycocyanin weakens the phosphorylation of MAPK family proteins and inhibits the transition of cells from G1 phase to S phase of the cell cycle by scavenging ROS and reducing the expression of CyclinD1, so as to inhibit the excessive proliferation of cells caused by Hp infection. Phycocyanin also regulates the NF-κB signaling pathway. IκB-α, nuclear factor kappa-B kinase alpha; p-IκB-α, phospho-IκB-α; ROS, Reactive oxygen species; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa gene binding; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase.