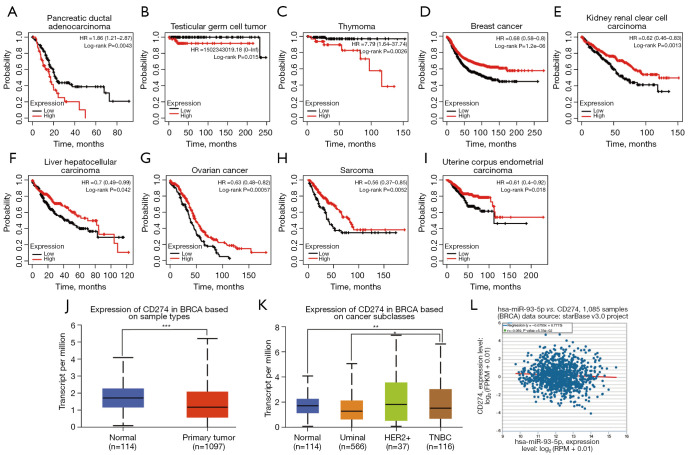
Figure 4.
PD-L1 generates differential prognostic outcomes in various tumors, and expression of PD-L is differentially decreased in BRCA in distinct subtypes of BRCA. (A-C) High expression of PD-L1 resulted in poor prognosis in breast cancer, head-neck squamous cell carcinoma, lung adenocarcinoma, lung squamous cell carcinoma, ovarian cancer, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, and thymoma according to Kaplan-Meier Plotter datasets. (D-I) High expression of PD-L1 conveyed good prognosis in breast cancer, kidney renal clear cell carcinoma, liver hepatocellular carcinoma, ovarian cancer, sarcoma, and uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma according to Kaplan-Meier Plotter datasets. (J) PD-L1 was decreased in BRCA according to UALCAN datasets. (K) PD-L1 was decreased in luminal and triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) subtypes of BRCA according to UALCAN datasets (P<0.01). (L) PD-L1 was negatively correlated with miR-93-5p, but the difference was not statistically significant. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. BRCA, breast cancer.