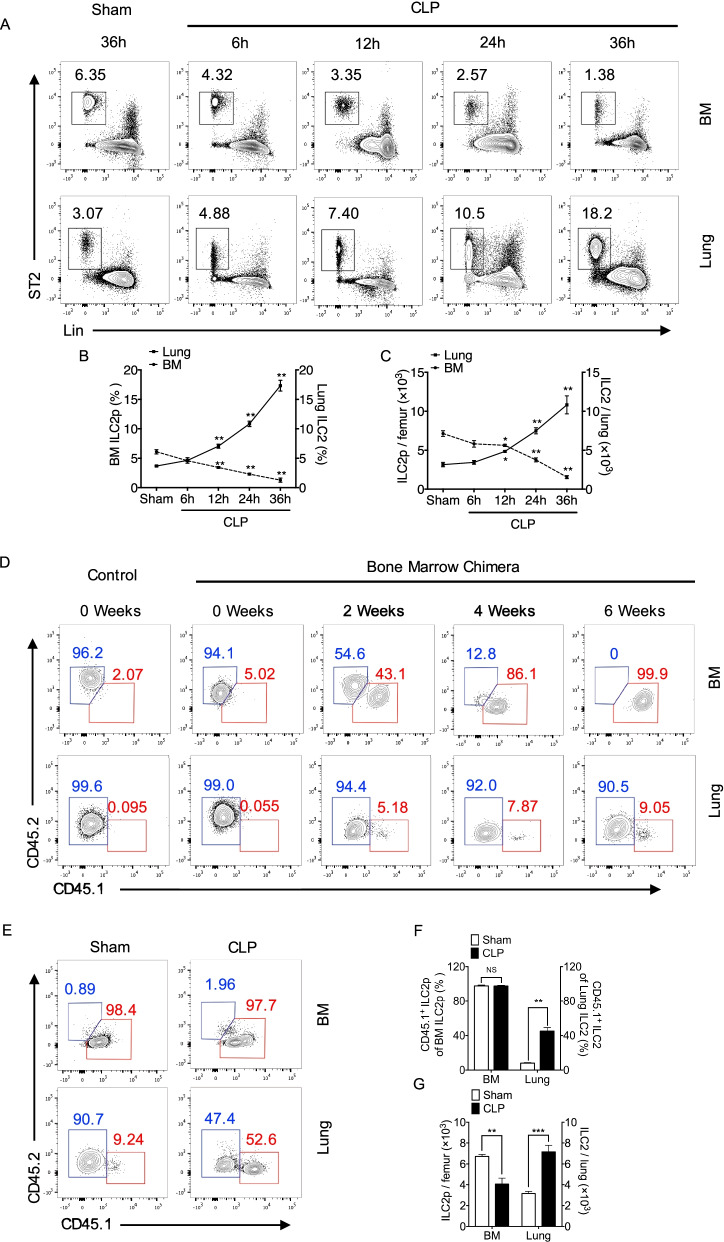
Fig. 1.
ILC2 egress from BM following sepsis. A Representative flow cytometry plots showing percentages of ILC2p in BM and ILC2 in lung of WT mice after sham surgery (36 h) and at 6, 12, 24, and 36 h after CLP (n = 5 mice/group). B Line graph showing BM ILC2p (left Y-axis) and lung ILC2 (right Y-axis) frequency at time points up to 36 h after CLP (n = 5 mice/group). C The absolute number of BM ILC2p (left Y-axis) and lung ILC2 (right Y-axis) at time points up to 36 h after CLP (n = 5 mice/group). D Representative flow cytometry plots showing frequencies of CD45.1 and CD45.2 of ILC2 in bone marrow and lung from bone marrow chimera mice (n = 3 mice/group). E Representative flow cytometry plots showing frequencies of CD45.1 and CD45.2 of ILC2 in bone marrow and lung from bone marrow chimera mice at 24 h after sham surgery or CLP (n = 4–5 mice/group). F The frequencies of CD45.1+ ILC2 in bone marrow (left Y-axis) and lung (right Y-axis) at 24 h after CLP (n = 4–5 mice/group). G The absolute number of BM ILC2p (left Y-axis) and lung ILC2 (right Y-axis) at 24 h after CLP in chimera septic mice (n = 4–5 mice/group). Data are shown as mean ± SEM. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, NS = not significant