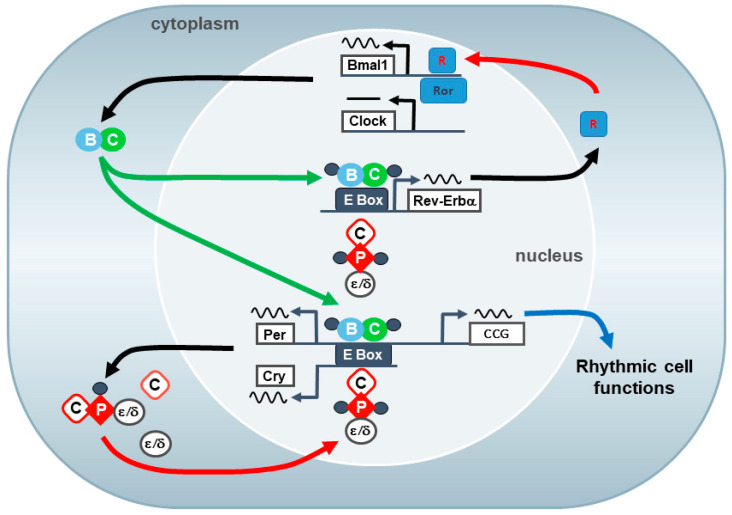
Figure 2.
The molecular clockwork: The molecular clockwork consists of autoregulatory transcriptional/translational feedback loops of clock genes that produce a 24-h (circadian) rhythm in gene expression and cell function. The core clock loop comprises the two transcription factors CLOCK (C) and BMAL1 (B) in addition to two families of gene expression inhibitors: the PERs and the CRYs. The CLOCK and BMAL1 complex activates the transcription of the Period (Per) and cryptochrome (Cry) genes and clock controlled genes (ccg) via E-box (like) enhancer elements. The Per (P) and Cry proteins (C) form a repressor complex that also comprises casein kinase 1ε or δ (ε, δ). After translocation into the nucleus, the repressor complex inhibits CLOCK:BMAL1-mediated transcription. A new cycle starts after ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of the repressor complex. An accessory feedback loop, including the orphan nuclear receptors REV-ERBα and RORα, modulate the core loop via binding to ROR enhancer elements and regulation of the Bmal1 gene [Reprinted with permission from ref. [2]. Copyright 2013 Springer Nature, after [4]].