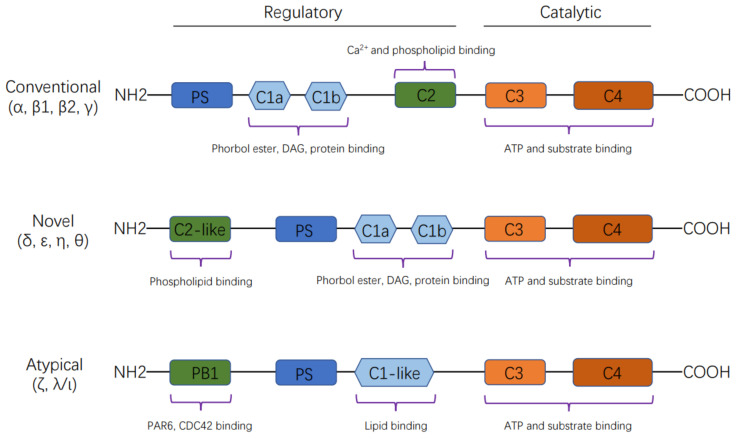
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the structure of protein kinase C (PKC) isoforms. The PKC family members are classified into three subfamilies according to their cofactor dependence: (i) conventional or classical PKC isozymes (cPKCs), including PKCα, PKCβ1, PKCβ2 and PKCγ, which are calcium-dependent and activated by both diacylglycerol (DAG) and phosphatidylserine (PS); (ii) novel PKC isozymes (nPKCs), including PKCδ, PKCε, PKCη and PKCθ, which are calcium-independent and regulated by DAG and PS; and (iii) atypical PKC isozymes (aPKCs), including PKCζ and PKCλ/ι, which are calcium-independent and do not require DAG for activation, although PS can regulate their activity.