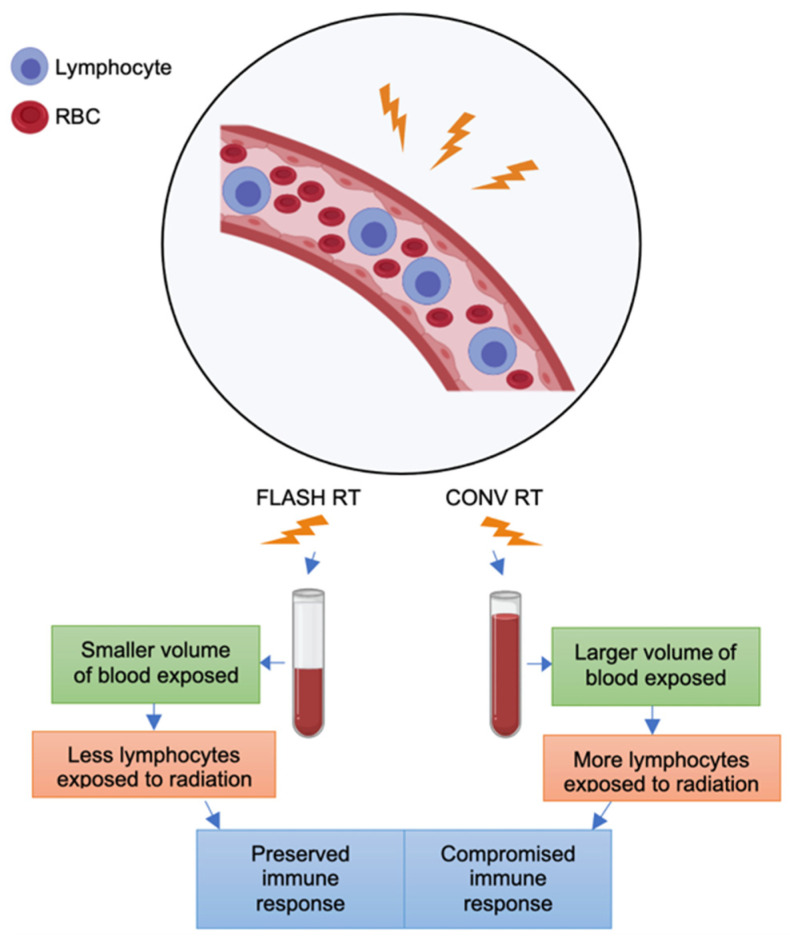
Figure 2.
Immune hypothesis for the FLASH effect. Lymphocytes circulating within blood vessels are an important component of the immune response that influences tumor suppression. According to the immune hypothesis, the higher dose rates characteristic of FLASH-RT allow exposure of a much smaller volume of blood to radiation than CONV-RT. As a result, a higher number of circulating lymphocytes will survive and the immune response critical for tumor suppression is preserved to a greater degree. In contrast, the lower dose rates used in CONV-RT allow exposure of larger blood volumes circulating through the radiation field, leading to a significant loss of lymphocytes and a compromised immune response.