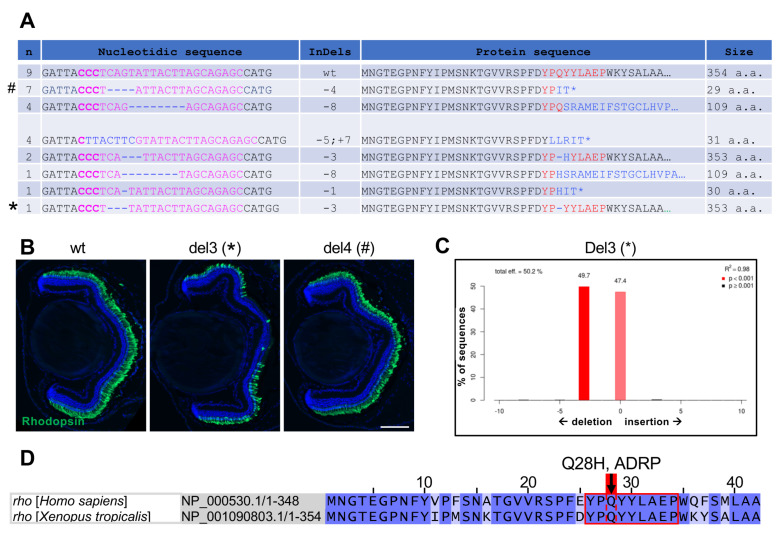
Figure 4.
Characterization of F1 X. tropicalis rho mutants. (A) Genomic sequences retrieved from F1 X. tropicalis rho mutants. The left column indicates the number of tadpoles harbouring the corresponding sequence. The targeted region is shown in pink with PAM in bold, while indels are in blue. The right column indicates the resulting protein sequence and its size (number of amino acids). (B) Immunofluorescence analysis of Rhodopsin expression on retinal sections from stage 45 wild-type and F1 individuals. Del3 and del4 tadpoles bear the sequences depicted in A with * (leading to lack of glutamine 28) and # (leading to a truncated protein), respectively. Cell nuclei are counterstained with Hoechst (blue). (C) TIDE analysis of the del3 rho mutant showing the presence of a wild-type and a mutated allele. (D) Illustration of Homo sapiens and X. tropicalis Rhodopsin protein sequences (amino acids 1 to 42). The region targeted by the rho sgRNA (red square) is conserved between the two species and includes glutamine 28, whose mutation Q28H was found in patients with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa (ADRP). Scale bar: 100 µm.