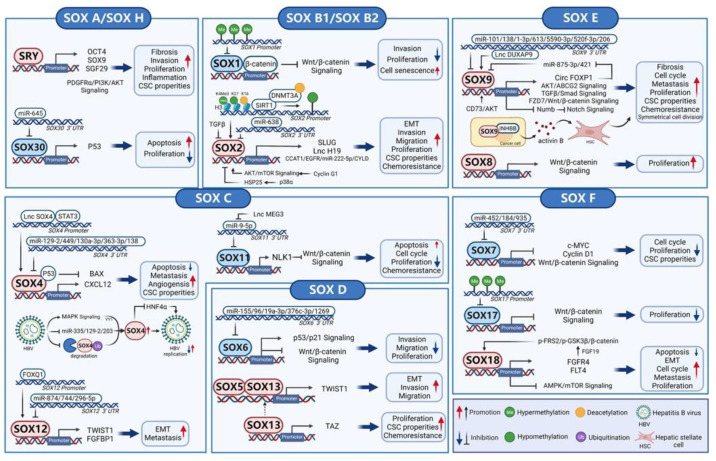
Figure 2.
The roles and molecular mechanisms of SOX transcription factors in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). SOX members serve as master tumor drivers or suppressors to transcriptionally regulate key downstream targets or signaling pathways, therefore controlling the initiation and progression of HCC. Simultaneously, the dysregulated SOX expression is frequently observed in HCC, which is mainly attributed to promoter hypermethylation, signaling pathway regulation, and post-transcriptional modulation by miRNAs (microRNAs). This diagram was created by BioRender.com (accessed on: 28 November 2021). The red box represents tumor driver, and the blue box represents tumor suppressor. Abbreviations: SOX: Sex-determining region Y-related high-mobility group box; SRY: Sex-determining region Y; CSC: Cancer stem cell; 3′UTR: 3′ untranslated region; H3: Histone 3; EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition.