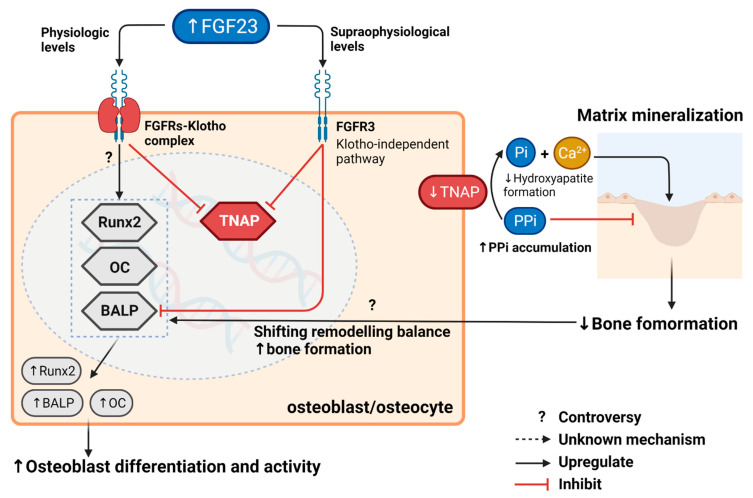
Figure 2.
Regulation of FGF23 and its autocrine/paracrine effects on bone formation. In supra physiologic conditions, FGF23 acts directly on FGFR3 in a Klotho-independent manner, thereby inhibiting bone formation. Increased FGF23 suppresses differentiated osteoblast activity and TNAP transcription, which subsequently causes PPi accumulation in the ECM and inhibits matrix mineralization. In physiological conditions, the actions of FGF23 on canonical receptors (FGFRs-Klotho complex) also downregulate TNAP, decreasing matrix mineralization. However, the upregulation of osteoblastic markers in these conditions may be caused by the shifting of remodelling balance toward bone formation or direct action of FGF23 via canonical receptors. The symbol “?” and dash lines denote issues of controversy and unknown mechanisms, respectively. This figure was generated with publication licensed by BioRender, Toronto, ON, Canada (Agreement number: VC237SOKSX, 19 November 2021). Abbreviations: BALP, Specific bone Alkaline phosphatase; FGF23, Fibroblast growth factor 23; Pi, Inorganic phosphate; PPi, Pyrophosphate; Runx2, Runt-related transcription factor 2; TNAP, Tissue nonspecific alkaline phosphatase; OC, Osteocalcin.