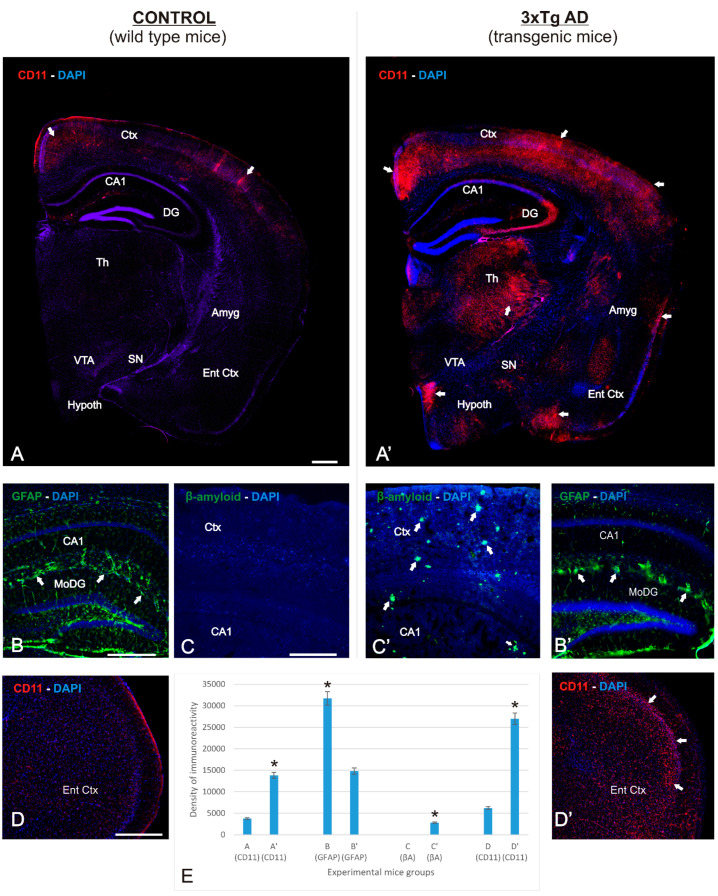
Figure 1.
Immunolocalization of various markers in the APP/BIN1/COPS5 3xTg-AD mouse brain. Photomicrographs of different brain regions from wild-type (n = 4) and APP/BIN1/COPS5 3xTg-AD (n = 4) mice showing histopathological lesions identified via immunohistochemistry. ((A–D), (A’–D’)) Transverse sections of right half-brain (A,A’), dentate gyrus (B,B’), hippocampus (C,C’), and entorhinal cortex brain levels of wild-type mice (A–C) and APP/BIN1/COPS5 3xTg-AD mice (A’–C’), showing strong differences in expression density. (A,A’) Hemi-brain sections showing a basal level of the inflammatory marker CD11b in wild-type mice, contrasting with a highly-differentiated agglomeration pattern of immunoreactivity in the APP/BIN1/COPS5 3xTg-AD mouse brain (white arrows). (B,B’) High magnification of the dentate gyrus showing a marked reduction of GFAP-immunoreactive cells in the APP/BIN1/COPS5 3xTg-AD mouse brain, forming reactive clusters ((B’); white arrows) that are absent in wild-type control sections (B). (C,C’) A high density of β-amyloid plaques (arrows in (C’)) is found in the APP/BIN1/COPS5 3xTg-AD mouse brain compared to controls (C), demonstrating severe neurodegeneration in transgenic mice. (D,D’) High magnification of the entorhinal cortex showing stronger CD11b immunoreactivity in the APP/BIN1/COPS5 3xTg-AD mouse brain than in controls (D’). (E) Quantification of data indicating the average percentage of immunoreactive markers in the experimental groups. * p < 0.05. Scale bars, 100 μm. Amyg, amygdala; βA, β-amyloid; CA1, hippocampal formation; CD11b, inflammatory marker; Ctx, cortex; DAPI, nuclear marker; DG, dentate gyrus; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; Th, thalamus; Ent Ctx, entorhinal cortex; Hypoth, hypothalamus; SN, substantia nigra; VTA, ventral tegmental area.