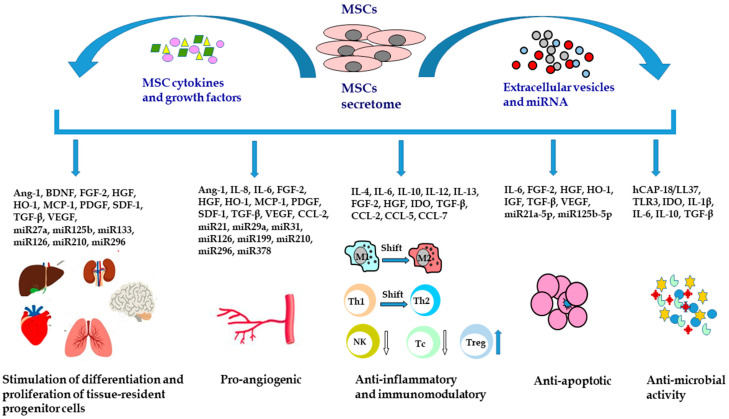
Figure 2.
Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells secretome and its therapeutic activity. MSCs can stimulate the differentiation and proliferation of tissue-resident progenitor cells, induce angiogenesis, modulate the inflammatory response, prevent cell apoptosis, and exert antimicrobial activity. Ang-1, angiopoietin 1; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; CCL-2, C-C motif chemokine ligand 2; CCL-5, C-C motif chemokine ligand 5; CCL-7, C-C motif chemokine ligand 7; FGF-2, fibroblast growth factor 2; hCAP18/LL37, human cationic antimicrobial protein; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; IDO, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; IGF, insulin-like growth factor; IL, interleukin; M1, M1 macrophages; M2, M2 macrophages; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; miR, microRNA; MSCs, mesenchymal stem cells; NK, natural killer cells; PDGF, platelet derived growth factor; SDF-1, stromal cell-derived factor 1; Tc, cytotoxic T cells; Th1, T helper cells type 1; Th2, T helper cells type 2; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β; TLR3, toll-like receptor 3; Treg, regulatory T cells; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.