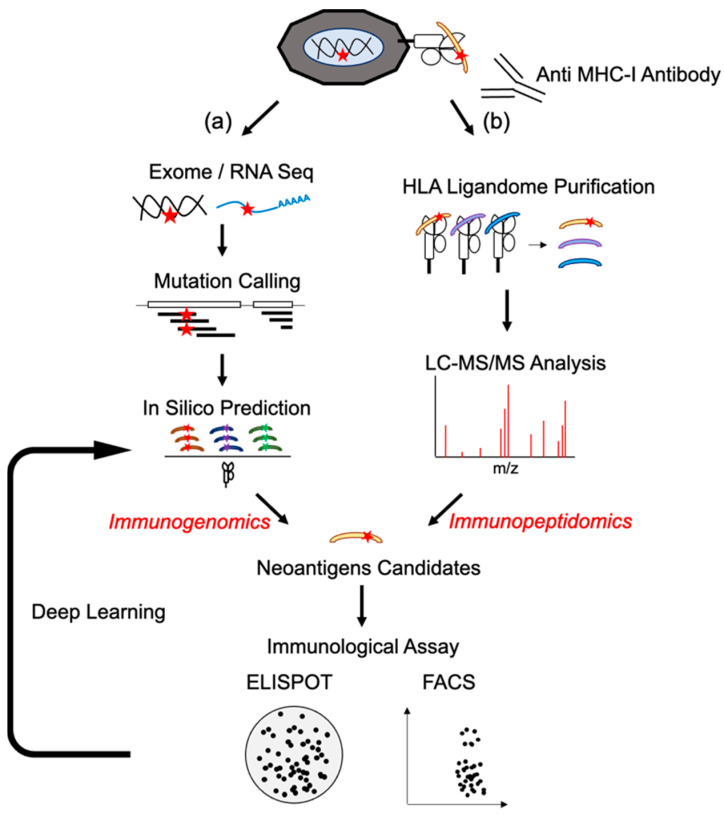
Figure 2.
Neoantigen identification by immunogenomic or immunopeptidomic method. Tumor biopsy samples are analyzed by immunogenomic or immunopeptidomic method. (a) In immunogenomic method, tumor and matched germinal tissues are subjected to exome and tumor RNA-seq to detect somatic mutations in expressed genes. Overlapping missense or indel mutation peptide sequences are analyzed to predict affinity to each MHC-I allele. (b) In the immunopeptidomic method, tumor tissues are lysed, and peptide/MHC-I complexes are purified by immunoprecipitation using anti-MHC-I antibodies. Binding peptides are eluted and separated by size. Then, mass spectrometry is performed to determine molecular weight and identifying corresponding mutated peptides. Using candidate neoantigen peptides, T cell responses are investigated by evaluating cytokine production, activation marker expression, and tetramer staining. Validated neoantigen peptide data are subjected to machine learning analysis.