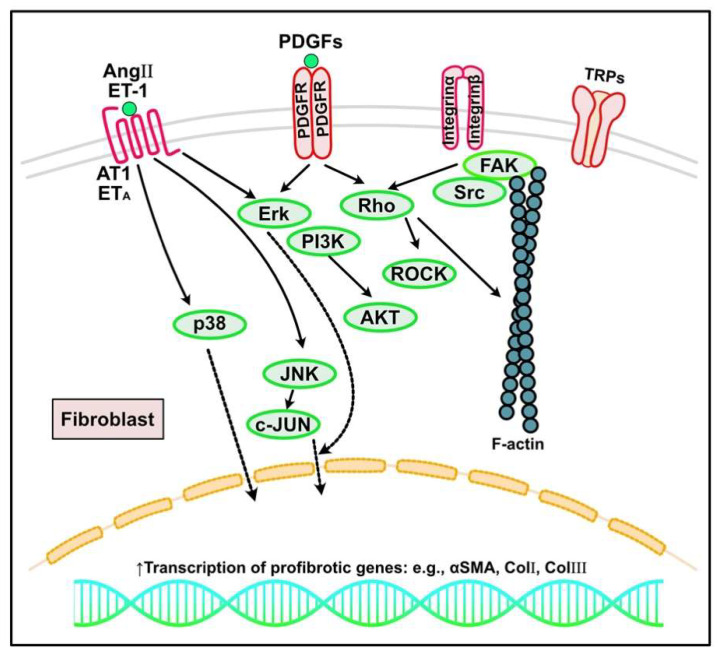
Figure 4.
Other signaling pathways regulating cardiac fibrosis. In response to increased mechanical stress and cardiac injury, inflammatory signaling, growth factors (e.g., platelet-derived growth factors (PDGFs)), neurohumoral pathways (e.g., angiotensin (Ang) II, endothelin (ET)-1), and mechanosensitive pathways mediated by integrins and ion channels such as transient receptor potential cation channels (TRPs) can activate fibroblasts into myofibroblasts, leading to excess extracellular matrix protein deposition and cardiac fibrosis. AT1, angiotensin type 1 receptor; PDGFR, PDGF receptor; ERK, extracellular signal regulated kinase; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; JNK, c-JUN N-terminal kinase; αSMA, α-smooth muscle actin; ROCK, Rho-associated protein kinases; FAK, focal adhesion kinase.