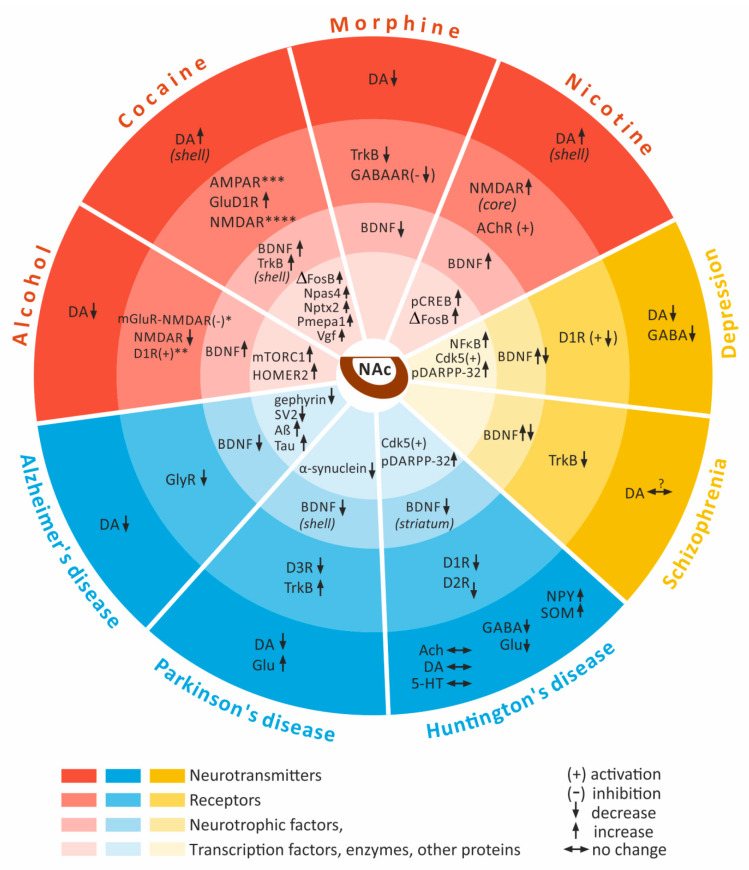
Figure 1.
Psychostimulant-induced and related mental illnesses and neurodegenerative diseases changes to the expression and activation level of different neuronal factors in the nucleus accumbens. * inhibition of group I mGluR-mediated potentiation of NMDAR, ** enhancement of excitatory synaptic transmission onto D1R+ neurons, *** long-term changes in AMPAR-dependent synaptic efficacy, **** impairment of NMDAR-dependent long-term potentiation and long-term depression at glutamatergic synapses. Abbreviations: Aß—amyloid ß; ACh—acetylcholine; AChR—acetylcholine receptor; AMPAR—α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid-type glutamate receptor; BDNF—brain-derived neurotrophic factor; Cdk5—cyclin-dependent kinase 5; DA—dopamine; DARPP-32—cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein 32; D1R—dopamine D1 receptor; D2R—dopamine D2 receptor; D3R—dopamin D3 receptor; GABA—γ-aminobutyric acid; GABAAR γ—aminobutyric acid type A receptor; Glu—glutamate; GluD1R—glutamate delta-1 receptor; GlyR—glycine receptor; HOMER2—Homer scaffolding protein 2; mGluR—metabotropic glutamate receptor; mTOR1—mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1; NFκB—Nuclear factor kappa B; NMDAR—N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; Npas4—neuronal PAS domain protein 4; Nptx2—neuronal pentraxin 2; NPY—neuropeptide Y; pCREB—phosphorylated adenosine 3′5′ cyclic monophosphate response element binding protein; Pmepa1—prostate transmembrane protein, androgen induced 1; SOM—somatostatin; TrkB—tropomyosin receptor kinase B; 5-HT—serotonin.