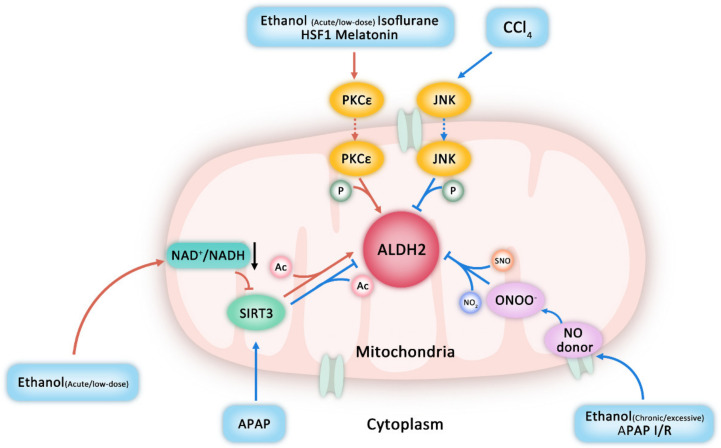
Figure 4.
Effect of protein post-translational modifications (PTMs) on ALDH activity. Ethanol (acute/low-dose), isoflurane, heat shock factor 1 (HSF1), and melatonin can lead to phosphorylation and activation of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) by activating phosphatidylinositol protein kinase C epsilon (PKCε). ALDH2 can also be activated by its acetylation increased by the inactivation of sirtuin 3 (SIRT3) stimulated by ethanol (acute/low-dose). The phosphorylation of ALDH2 promoted by c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) under carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) exposure as well as the S-nitrosylation and tyrosine nitration of ALDH2 stimulated by ethanol (chronic or excessive abuse), acetaminophen (N-acetyl-p-aminophenol [APAP]), nitric oxide (NO) donor, and ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury can inhibit ALDH2 activity. P = phosphorylation; Ac = acetylation; SNO = S-nitrosylation; NO2 = nitration.