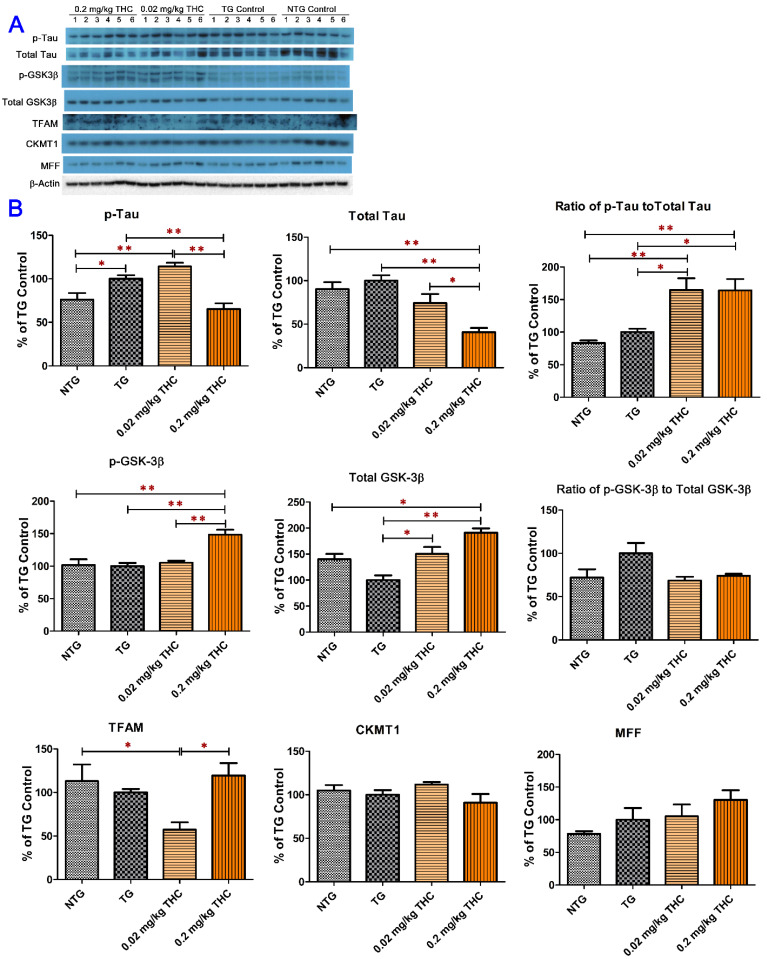
Figure 7.
Evaluation of the effect of THC on the protein expression of phospho-tau, total tau, phospho-GSK-3β, total GSK-3β, TFAM, CKMT1, and MFF in brain homogenates using western blot analysis. (A) Western blot images of the expression of total and phosphorylated Tau and GSK-3β, TFAM, CKMT1, and MFF proteins in individual brain homogenate samples collected from the control NTG (N = 6), control TG (N = 6), 0.02 mg/kg (N = 6), and 0.2 mg/kg (N = 6) THC treatment groups. Detection of β-actin was used to ensure equal sample loading per lane. (B) Relative immunoreactive band intensities are expressed as percent change over the average signal value in the control TG mouse brain homogenates. THC treatment at 0.2 mg/kg significantly decreased the expression levels of phospho-tau and total Tau and increased the expression levels of phospho-GSK3β and total GSK3β compared with the vehicle treatment in APP/PS1 mice. THC treatment at either 0.02 mg/kg or 0.2 mg/kg had no significant effect on the protein levels of TFAM, CKMT1, and MFF in brain homogenates. Data are presented as mean ± SD (N = 6 for each study group). SD is denoted by the error bars. * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 compared between the control NTG mice, control APP/PS1 mice, and APP/PS1 mice treatment with 0.02 and 0.2 mg/kg THC using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey–Kramer post hoc multiple comparison test.