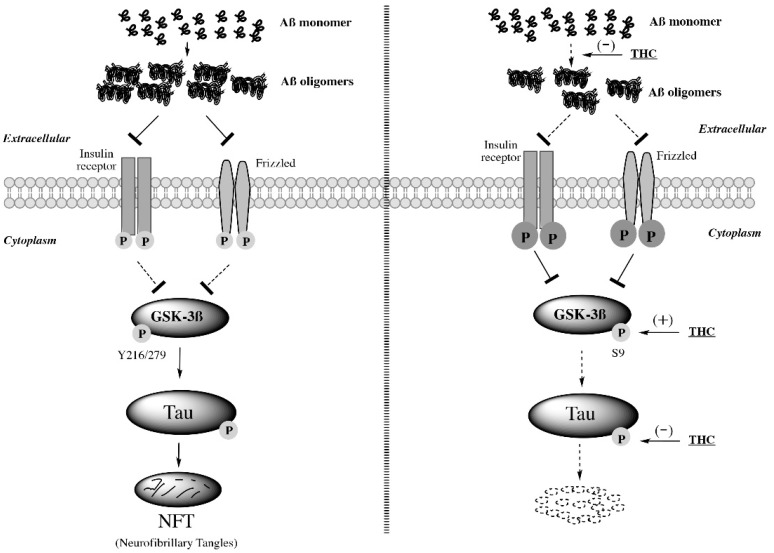
Figure 10.
Inhibitory effect of low-dose THC treatment on Aβ aggregation, GSK-3β activity, and tau phosphorylation in the brain. Low-dose THC prevents Aβ monomers from forming Aβ oligomers and alleviates the antagonistic effect of Aβ oligomers on insulin receptors and Frizzled so that insulin receptors and Frizzled are able to downregulate GSK-3β activity. Moreover, low-dose THC may decrease GSK-3β activity directly by increasing the Ser9 phosphorylation of GSK-3β. Since the increased GSK-3β activity promotes tau phosphorylation, it is likely that the inhibitory effect of THC on tau phosphorylation is in part attributable to the THC-induced Ser9 phosphorylation of GSK-3β.