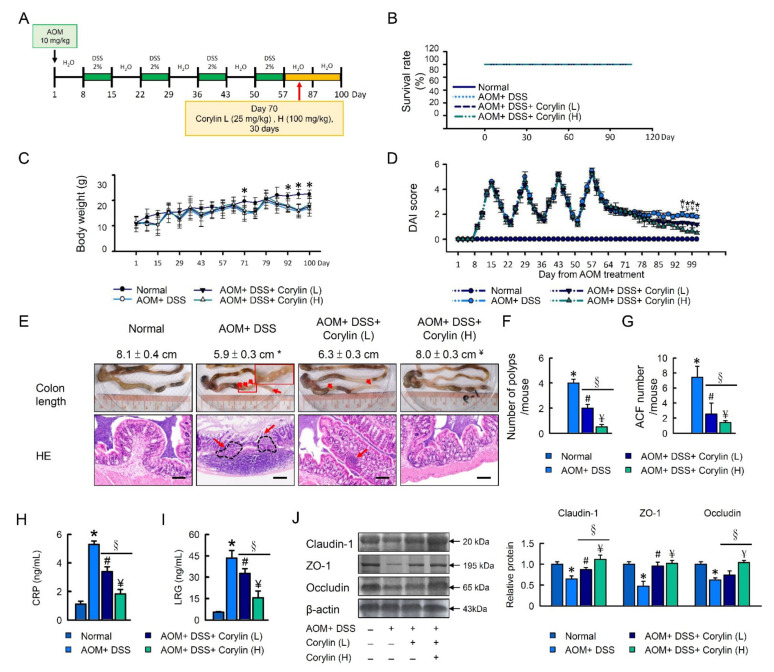
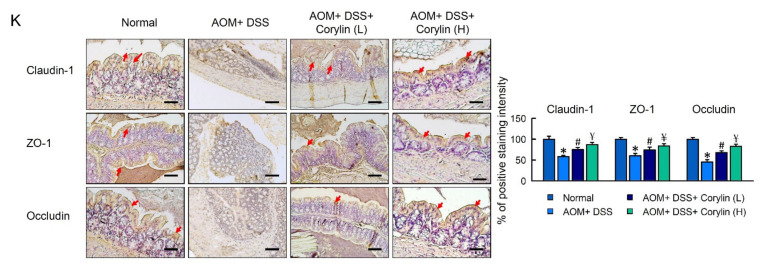
Figure 5.
Corylin ameliorates AOM/DSS-induced-colitis-associated colorectal cancer in mice. (A) Schematic of the recurring model of AOM/DSS-induced-colitis-associated colorectal cancer. (B) Survival rate in experimental mice. (C) Body weight curves of WT mice treated with AOM/DSS and corylin. (D) Disease activity index (DAI) score in experimental mice. (E) Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin staining and of colon tissues of mice. Red arrows highlight the damage. Scale bar: 100 μm. Colon length from experimental mice. (F) Number of polyps, and (G) ACF in WT mice treated with AOM/DSS and corylin. (H) CRP and (I) LRG levels in experimental mice. (J) Western blot analysis of claudin-1, ZO-1, occludin, and β-actin (loading control) in colon homogenates. Right graph indicates quantification relative to β-actin. (K) Expression analysis by immunohistochemical staining of claudin-1, ZO-1, and occludin in mice after the indicated treatment. Tissue staining, as quantified by either stain intensity, is represented on the left-hand vertical axis in each graph. Results represent mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05, Normal compared with AOM/DSS; # p < 0.05, AOM/DSS compared with AOM/DSS + Corylin (L); ¥ p < 0.05, AOM/DSS compared with AOM/DSS + Corylin (H); § p < 0.05, DSS + Corylin (L) compared with DSS + Corylin (H). AOM, azoxymethane; DSS, dextran sodium sulfate; ACF, aberrant crypt foci; ZO-1, zonula occludens-1; CRP, C-reactive protein; LRG, leucine-rich alpha 2 glycoprotein.