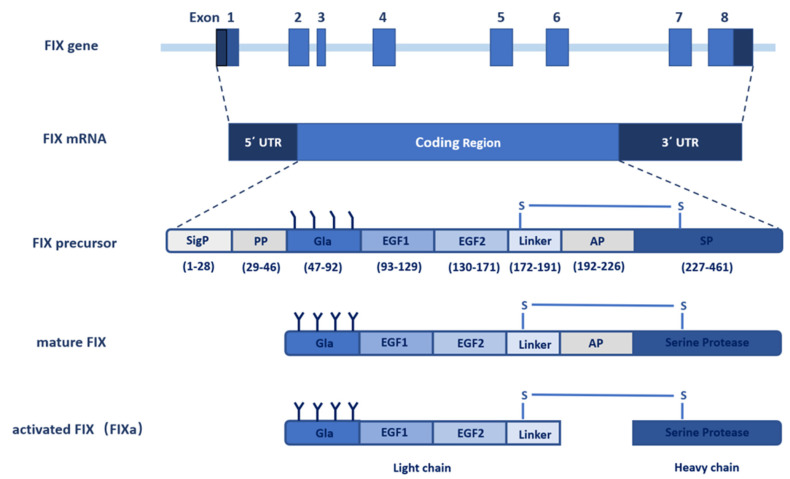
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the F9 gene structure and FIX protein processing. The F9 gene contains eight exons and seven introns that transcribe into a 2.8 kb mRNA with 5′ and 3′ noncoding flanking sequence. The coding sequence translates into the FIX precursor, including the signal peptide, propeptide, Gla domain, EGF1 domain, EGF2 domain, linker, activation peptide (AP), and serine protease (SP) domain. The FIX precursor undergoes multiple post-translational modifications, especially γ-carboxylation, and is further processed to form the mature FIX secreted to the extracellular space. The inactive FIX zymogen is activated by the cleavage of the activation peptide to FIXa, which contains a light chain and a heavy chain linked by a disulfide bond.