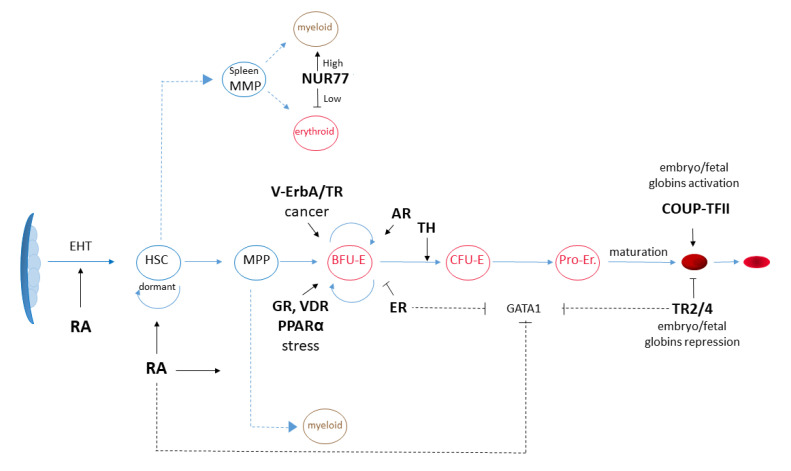
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the major NR signaling pathways affecting erythropoiesis and of their role in erythroid cell lineage specification and maturation. EHT: endothelial hematopoietic transition; HSC: hematopoietic stem cell; MMP: multiple myeloid progenitor; BFU-E: blast-forming unit, erythroid; CFU-E: colony-forming unit, erythroid; Pro Er: proerythroblast; MPPS: splenic multipotent progenitors; RA: retinoic acid; ER: estrogen receptor; AR: androgen receptor; GR: glucocorticoid receptor; GR: granulocytes; VDR: vitamin D receptor; PPARα: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; v-ErbA: mutated version of thyroid hormone receptor-α, responsible for avian erythroblastosis; T3: triiodothyronine; TR2/4: testicular receptors 2/4; COUP-TFII: chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor II.