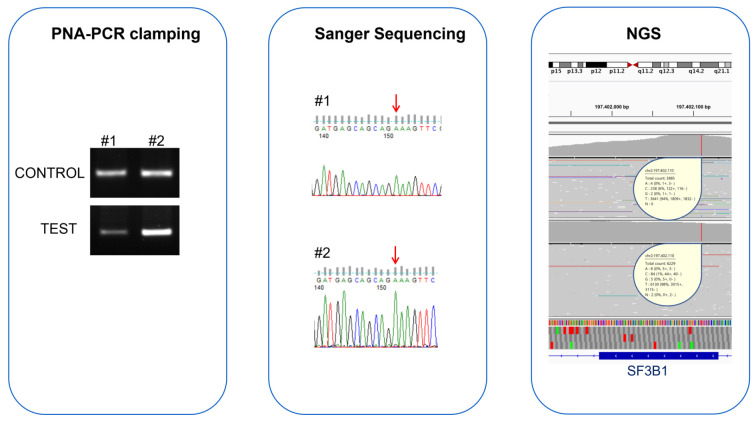
Figure 3.
Comparison of PNA-PCR clamping, Sanger sequencing, and NGS for the evaluation of SF3B1 status in two MDS patients with contrasting results. The electrophoretic runs of PNA-PCR clamping, carried out in the absence (CONTROL) and presence (TEST) of the PNA probe, showed amplification in both the samples, indicating the presence of the SF3B1 p.Lys700Glu mutation in these patients. In contrast, Sanger sequencing chromatograms showed the presence of only one allele (red arrows); the nucleotide “A” indicates that both patients were WT for SF3B1 p.Lys700Glu mutation. NGS confirmed the PNA-PCR clamping result, indicating that these samples contained SF3B1 p.Lys700Glu with mutation percentages of 1.3% and 6.1%, respectively. Both samples had mutation percentages lower than the Sanger sequencing LoD, but they were detected by PNA-PCR clamping methodology.