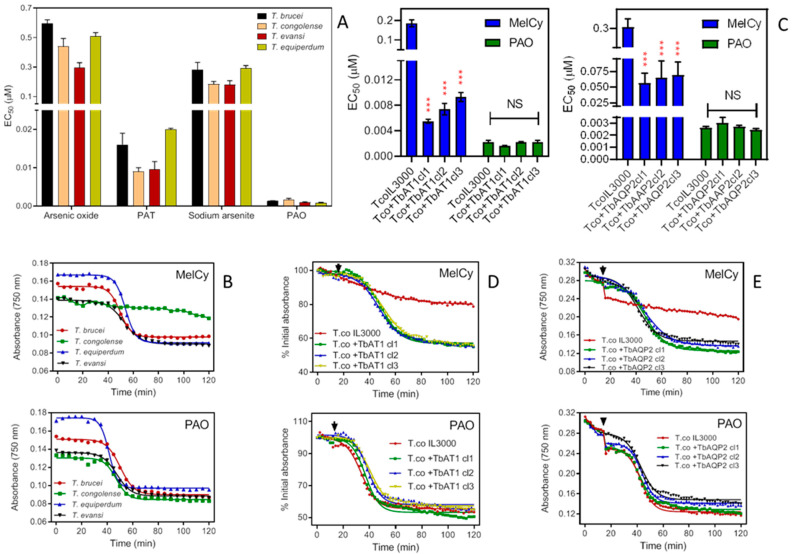
Figure 6.
Effects of arsenicals on various Trypanosoma species. (A) Sensitivity of four species of animal trypanosomes to arsenicals and an antimonial. Drug sensitivity is represented as EC50 averages of 3–5 independent Alamar Blue experiments (means ± standard error of mean). The differences in the EC50’s of arsenic oxide, sodium arsenite and phenylarsine oxide (PAO) and potassium antimony tartrate (PAT) between T. brucei, T. evansi and T. equiperdum are only marginal. (B) Effects of 3.3 µM melarsomine (upper frame) or 0.33 µM PAO (lower frame) on the absorbance of trypanosomes over time. Measurements of absorbance were carried out, taking readings every 5 min with a PHERAstar microplate reader at 750 nm, and presented as averages of a single experiment performed in triplicates. Upper frame: time to 50% lysis was 49.5 ± 0.4 min for T. b. brucei, 53.7 ± 0.19 min for T. equiperdum and 52.7 ± 0.6 min for T. evansi. Lines were calculated by non-linear regression using an equation for a sigmoid curve with variable slope (Prism 9). Lower frame: 50% lysis was at 50.2 ± 0.5 min, 47.0 ± 0.7 min, 41.5 ± 0.3 min and 47.6 ± 0.5 min for T. b. brucei, T. congolense, T. equiperdum and T. evansi, respectively. (C) Effects of melarsomine (MelCy) and PAO on TcoIL3000 and the same cells expressing either TbAT1 or TbAQP2. Bars represent the averages and SEMs of three independent experiments. *** p < 0.001; NS, not significant. (D) Like frame B, using IL3000 and IL3000 expressing TbAT1. The drug was added at 15 min (arrowheads); readings were taken every 2 min. Symbols are averages of triplicate determinations. (E) Like frame D except with IL3000 expressing TbAQP2.