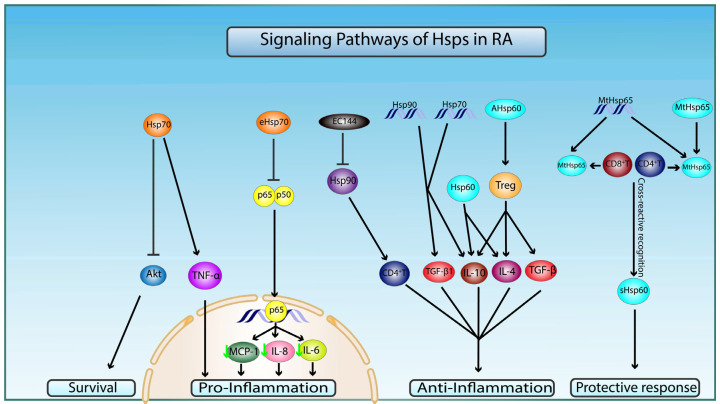
Figure 3.
Molecular mechanisms of Hsp60, 70, and 90 in pathophysiology of RA. Preimmunization with naked DNA of mycobacterial Hsp65 (MtHsp65) or MtHsp65 leads to recognition of Hsp65 and cross-reactive recognition of self-Hsp60 (sHsp60) epitopes by CD4+ and CD8+T cells, which confer protection in RA through a T-cell-mediated protective immune response. Intracellular Hsp60 and administration of arthritis-related Hsp60 T-cell epitope (AHsp60) can dampen RA-related inflammation by T-regulatory cells (Treg)-mediated stimulation of secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines TGF-β, IL-4, and IL-10. Hsp70 increases proinflammation and apoptosis by upregulating TNF-α and inhibiting pro-survival Akt signaling pathways, respectively. Hsp70 and Hsp90 DNA vaccination conferred anti-inflammatory protection via increase in anti-inflammatory cytokines TGF-β1 and IL-10. Extracellular Hsp70 (eHsp70) downregulates inflammatory processes by inhibiting nuclear translocation of NF-κB (p65/50) and transcription of proinflammatory cytokines MCP-1, IL-6, and IL-8 (green arrow indicates a decrease in gene expression). Target inhibition of Hsp90 by EC144 promotes the diminishment of CD4+T-cell-mediated immune response.