Table 1.
Isolated active compounds from secondary plant metabolites.
| No. | Active Compound | Structure | Categories | Source | Experiment Model | Therapeutic Target | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | β-carbolines |
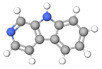
|
Alkaloid | Arenaria kansuensis | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice; in vitro: A549, RAW264 | Inhibiting NF-κB/p65 and EMT transition | [153] |
| 2. | Coelonin |
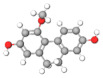
|
Dihydrophenanthrene | Bletilla striata | In vivo: BLM-induced PF rats | Anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic | [154] |
| 3. | Celastrol |
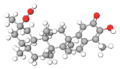
|
Triterpenoid | Tripterygium wilfordii and Celastrus regelii. | In vivo: BLM-induced PF rats; in vitro: A549 cells | TGF-β1/Smad2/3-mediated inhibition of EMT | [155] |
| 4. | Magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate (MgIG) |
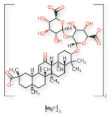
|
Triterpenoid saponin glycoside | Glycyrrhiza glabra | In vivo: radiation-induced PF mice; in vitro: human fetal lung fibroblasts-1 (HFL1) | Inhibiting fibroblast differentiation via p38MAPK/Akt/Nox4 pathway | [156] |
| 5. | Alpha-mangostin (α-MG) |
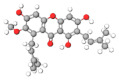
|
Xanthone | Mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana) | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice; in vitro: mouse primary lung fibroblasts (PLFs) | Inhibiting AMP-activated protein kinase | [157] |
| 6. | Gambogic acid |
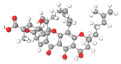
|
Xanthonoid | Garcinia hanburyi | In vivo: BLM-induced PF rats. In vitro: HLF-1, HPMECs, and A549 cells | Reversing EMT and suppress TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway | [158] |
| 7. | Salvianolic acid B (SAB) |
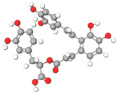
|
Polyphenol | Salviae miltiorrhiza | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice; in vitro: NIH/3T3 fibroblasts, MRC-5 fibroblasts, A549 cells | Inhibiting TGF-β signaling | [159] |
| 8. | Curcumin and curcumol |
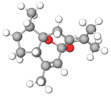
|
Curcuminoid | Rhizomes of Curcuma zedoaria | in vitro: human lung fibroblast (HLF) | Inhibiting collagen deposition via autophagy mechanism | [160] |
| 9. | Polydatin (PD) |
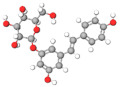
|
Resveratrol glucoside | Polygonum cuspidatum | In vivo: MP-induced PF mice; in vitro: BEAS-2B cells | NLRP3 inflammasome and NF-κB pathway | [161] |
| 10. | Gentiopicroside(GPS) |
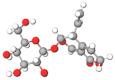
|
Secoiridoid glycoside | Gentianascabra, Gentiana lutea | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice; in vitro: A549 cells | Anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic via TGF-β-1 | [162] |
| 11. | Dioscin (Dio) |
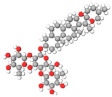
|
Steroidal saponin | Dioscorea nipponica Makino | In vivo: silica-induced PF mice; in vitro: RAW264.7 cell line, NIH-3T3 cell line | Inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines through ASK-1-p38/JNK signaling | [163] |
| 12. | β-sitosterol |
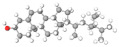
|
Phytosterols | stigma and style of maize (Zea mays) | In vitro: human lung adenocarcinoma epithelial cells, A549. | Suppression of EMT via the TGF-β1/Snail pathway | [164] |
| 13. | Asiatic Acid |
|
Triterpenoid | Centella Asiatica | In vivo: BLM-induced mice | Anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic | [165] |
| 14. | Andrographolide |
|
labdane diterpenoid lactone | Andrographis paniculata | In vivo: silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis mice | Anti-inflammatory and EMT transition | [166] |
| 15. | zingerone (vanillylacetone) |
|
Ketone | Zingiber officinale | In vivo: BLM-induced PF rats | Inhibiting NF-κB and MAPKs | [167] |
| 16. | Tetrandrine (TET-HP-β-CD) |
|
Alkaloid | Stephania tetrandra, S. Moore | In vivo: BLM-induced PF rats | Alleviating inflammation and fibrosis | [168] |
| 17. | Juglanin |
|
Flavonoid | Polygonum aviculare | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice | Inhibition of stimulator of interferon genes (Sting) signaling | [168] |
| 18. | Paeonol |
|
Phenols | Paeonia suffruticosa | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice | Inhibition of MAPKs/Smad3 signaling | [169] |
| 19. | Honokiol |
|
Neolignan | Magnolia officinalis | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice | Inhibiting EMT and TGF-β/Smad signaling both in vitro and in vivo | [170] |
| 20. | Phycocyanin |
|
Phycobilins | Cyanobacteria | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice | Attenuating PF via TLR2-MyD88-NFκB signaling | [171] |
| 21. | Schisandrin B |
|
Tanin | Schisandra chinensis | In vitro: A549 cells. BLM-induced PF mice | Attenuating BLM-induced PF via wingless/integrase-1 signaling | [172] |
| 22. | Morin |
|
Flavonoid | Maclura pomifera | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice | Anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory | [173] |
| 23. | Berberine |
|
Alkaloid | Chinese herbs | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice | Activation of PPAR-γ. Expression of HGF in the colon. | [174] |
| 24. | Zingerone |
|
Phenolics, Ketone | Zingiber officinale | In vivo: BLM-induced PF rats | Modulating the expression of TGF-β1 and iNOS | [175] |
| 25. | Glaucocalyxin A |
|
Diterpenoid | Rabdosia japonica | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice | Antagonism of leukocyte infiltration. Proinflammatory cytokine production. | [176] |
| 26. | Parthenolide |
|
Sesquiterpene | Tanacetum parthenium | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice; in vitro: primary lung fibroblast, HFL1 cells, A549 cells | Attenuating BLM-induced PF via NF-κB/Snail signaling | [177] |
| 27. | Oridonin |
|
Diterpenoid | Rabdosia rubesecens | In vitro: MRC5 cells, in vivo: BLM-induced PF mice | Regulating TGFβ/Smad pathway | [178] |
| 28. | Apigenin |
|
Flavonoid | Vegetables | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice | Anti-oxidative and PPARγ expression | [179] |
| 29. | Salvianolic acid B and sodium tanshinone IIA |
|
Phenolics | Salvia miltiorrhiza | In vitro: MR5 cells | Anti-inflammation and anti-fibrotic | [180] |
| 30. | Nimbolide |
|
Terpenoids | Azadirachta indica | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice; in vitro: TGF-beta induced cell line | Autophagy regulator through attenuation of EMT pathway | [181] |
| 31. | Perostilbene |
|
Polyphenol | Blueberries | In vivo: LPS-induced PF mice | Preventing fibrosis by suppressing oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis | [182] |
| 32. | Scutellarein |
|
Flavonoid | Scutellaria Lateriflora | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice; in vitro: human pulmonary fibroblast | Affecting fibroblast differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis | [183] |
| 33. | Sulforaphane |
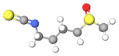
|
Isothiocyanates | Cruciferous vegetables | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice; in vitro: A549 cell, MRC-5 cell | Inhibiting EMT transition | [184] |
| 34. | Salvianolic acid B |
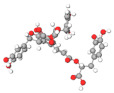
|
Phenolic acids | Salvia miltiorrhiza | In vivo: BLM-induced PF rats; in vitro: MRC-5 cells | Inhibiting myofibroblast trans-differentiation via upregulation of Nrf2 | [185] |
| 35. | GHK peptide |
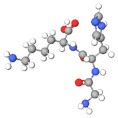
|
Tripeptide | Plasma protein | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice | Anti-oxidative and anti-inflammation | [186] |
| 36. | Glycyl-L-histidyl-l-lysine (GHK)-Cu |
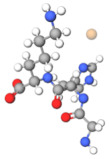
|
Tripeptide | Plasma protein | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice | Anti-oxidative and anti-inflammation | [187] |
| 37. | Myricetin |
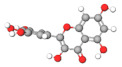
|
Flavonoid | Commercially purchase | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice; in vitro: human, mouse pulmonary epithelial cell, lung fibroblast cell | Inhibiting TGF-β1 via targeting HSP90β | [188] |
| 38. | Wedelolactone |
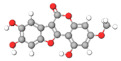
|
Coumarin | Eclipta prostrata | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice | Activation of AMPK and regulating Raf-MAPK pathway | [189] |
| 39. | Madecacassoside |
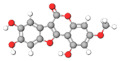
|
Pentacyclic triterpenoid | Centella asiatica | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice | Promoting hepatocyte growth factor in the colon via PPAR-γ | [190] |
| 40. | Rutin |
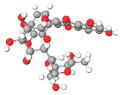
|
Flavonoid | Citrus plant | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice | Inhibiting TGF-β1-α/SMA/Col I and III pathway | [191] |
| 41. | Caffeine |
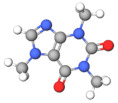
|
Alkaloid | Tea, coffee, cacao, etc. | ex vivo: precision-cut lung slice model; in vitro: epithelial and lung fibroblast cells | Inhibiting TGF-β activation | [192] |
| 42. | Emodin |
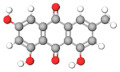
|
Anthraquinone | Rhubarb | In vivo: BLM-induced PF rats; in vitro: alveolar epithelial cell | Inhibiting EMT transition, TGF-β1, p-Smad2/3 | [193] |
| 43. | Rhapontin |
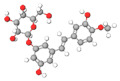
|
Stilbene glycosides | Rheum genus/ Rhubarb | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice; in vitro: primary lung fibroblast; LP-stimulated human THP-1 | Reducing collagen deposition, TGF-beta1, α-SMA, HIF-α expression | [194] |
| 44. | Hydroxysafflor yellow A (HSYA) |
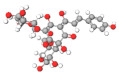
|
Flavonoid | Carthamus tinctorius | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice; in vitro: A549 cells | Reducing ECM deposition | [195] |
| 45. | Alantolactone and isoalatolactone |
|
Sesquiterpene lactone | Inula helenium L | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice; in vitro: TGF-β1-induced human lung fibroblasts. | Inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling pathway | [196] |
| 46. | 4-methoxyphenethylamine |
|
Biological amine | Pericarp of Citrus Reticulata | In vivo: BLM-induced PF rats model; in vitro: human embryonic lung fibroblast | Inhibiting TGF-β1 | [197] |
| 47. | Galangin |
|
Flavonoid | Galangal | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice | Attenuating EMT and inflammatory damage | [198] |
| 48. | Quercetin and Gallic acid |
|
Flavonoid | Quercetin and Gallic acid | In vivo: BLM-induced PF rats | Anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory | [199] |
| 49. | Rosavin |
|
Alcohol glycosides | Rhodiola rosea | In vivo: BLM-induced PF mice | Anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory | [200] |
| 50. | Ascorbic Acid |
|
Vitamin | Fruits | In vivo: PQ-induced PF | Reducing IL-6, IL-17a, TGF-beta | [201] |
| 51. | Quercetin |
|
Flavonoid | Diverse plant sources | Amiodarone intra-tracheal instillation | Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory | [202] |
The molecular structures of active compounds were generated from the online repository www.molview.org, accessed on 14 October 2021. Here, each color in molecules denotes each atom. Therefore, gray = carbon, white= hydrogen, red=oxygen, blue=nitrogen, and yellow=sulfur.
