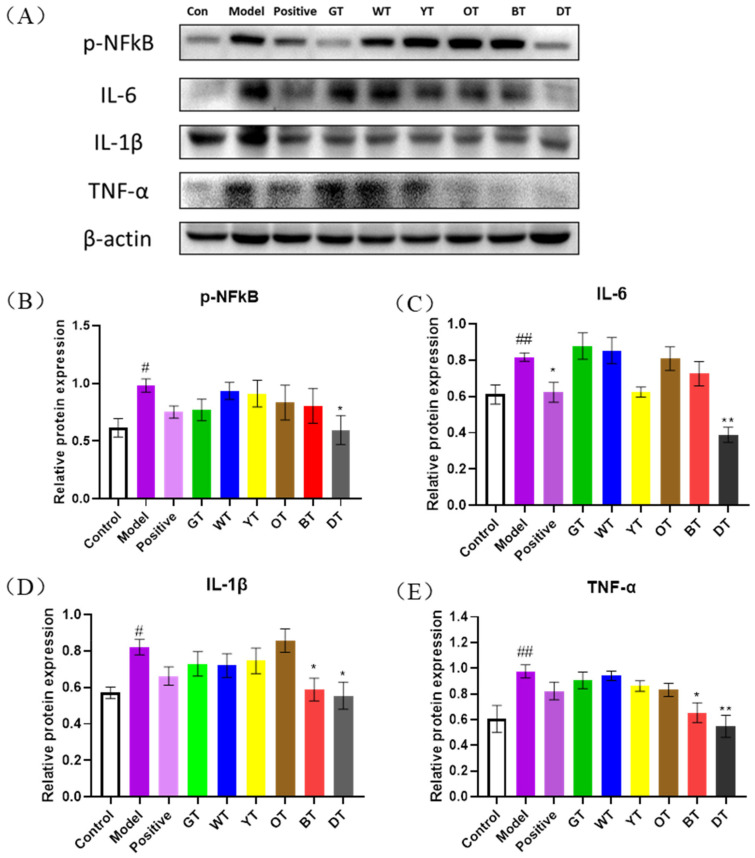
Figure 5.
Fermented tea inhibited CCl4-induced inflammation by blocking the NF-κB signaling pathway. (A) Immunoblot showing expression levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and p-NF-κB and the quantification of (B) p-NF-κB, (C) IL-6, (D) IL-1β, and (E) TNF-α. β-actin was the loading control. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments (n ≥ 5). # p < 0.05 and ## p < 0.01 versus control group; * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 Tea-treated versus the Model group.