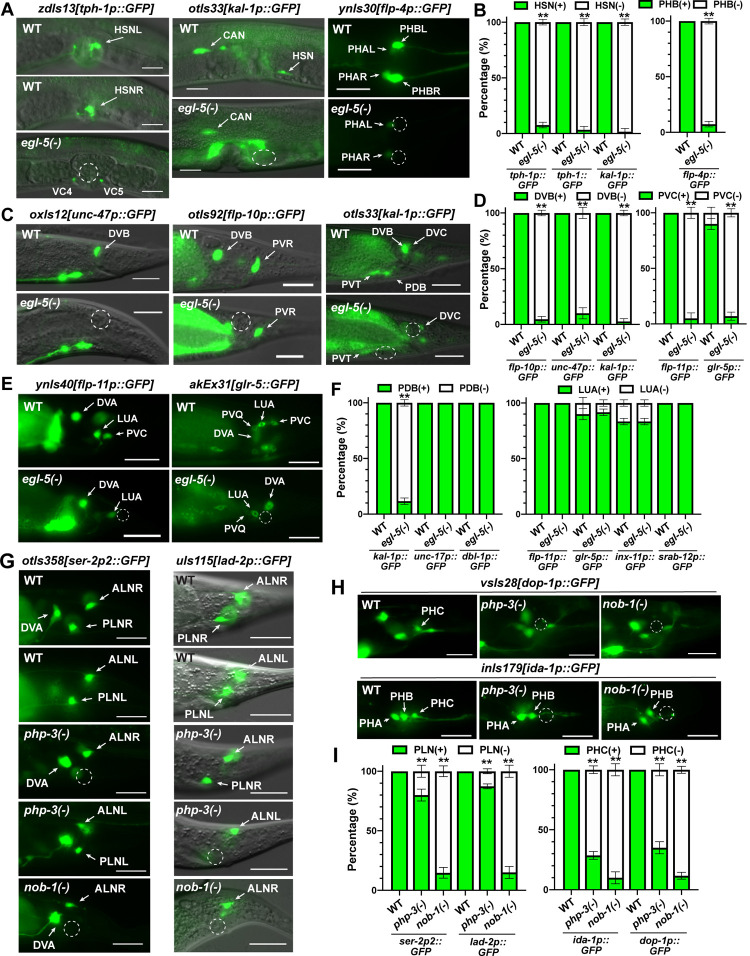
Fig 4. EGL-5, PHP-3, and NOB-1 regulates fate specification of tail neurons.
(A) The expression of fate markers tph-1 and kal-1 were lost in HSN in egl-5(u202) mutants; tph-1 was ectopically expressed in VC4 and VC5 neurons. Expression of PHB fate marker flp-4 was lost in egl-5 mutants. (B) The penetrance of the HSN and PHB marker expression; tph-1p::GFP and tph-1::GFP show the results of zdIs13 and mgIs42 expression, respectively. (C) The loss of fate markers unc-47, flp-10, and kal-1 in DVB neurons in egl-5 mutants; kal-1 expression was also lost in PDB neurons. (D) The penetrance of DVB and PVC marker expression. (E) The loss of PVC fate marker flp-11 and glr-5 expression in egl-5 mutants. (F) The penetrance of PDB and LUA marker expression. (G) The loss of ser-2 and lad-2 expression in PLN neurons in php-3(ok919) and nob-1(ct230) mutants. (H) The loss of dop-1 and ida-1 expression in PHC neurons in php-3 and nob-1 mutants. (I) The penetrance of PLN and PHC fate marker expression. Scale bars = 20 μm. Quantification shows mean ± SD for the percentage of cells showing expression from three biological replicates. Double asterisks indicate statistically significant difference (p < 0.01) between the mutants and the wild type in a Chi-square test.