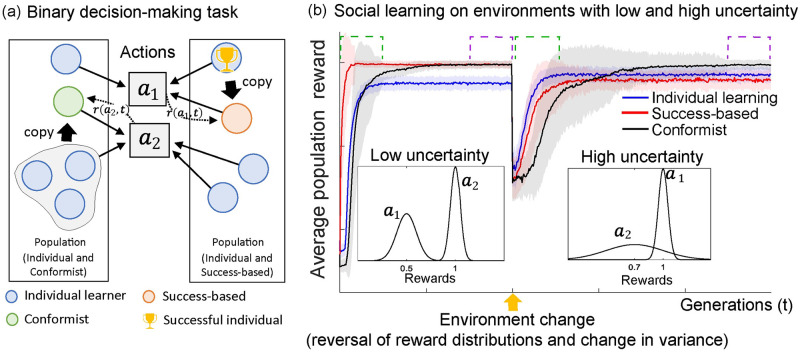
Fig 1. The learning process of populations of individual and social learners on a binary decision-making task.
(a) A population of individuals perform a binary decision-making task based on individual and social learning strategies and collect their rewards (r(aj, t)) based on their actions. The individual learners, modeled by a the ϵ-greedy algorithm [32] (see Section 4.2), can perform their actions based on their decision models that can be improved by experience. The social learners use success-based or conformist strategies to copy the actions of successful individuals or the majority respectively (see Section 4.3). (b) Binary decision-making task (2-armed bandit) is iteratively performed for a certain period of time with specified reward distributions that are unknown to the individuals. At some point, an environment change occurs by changing the reward distributions (a.k.a reward reversal). In earlier stages of the process (initial and after environment change, shown in green dash lines), populations with success-based social learning strategy achieves higher average population reward faster relative to the conformist strategy. In later stages of the process (shown in purple dashed lines), populations with success-based social learning strategy achieves higher average population reward in environments with low uncertainty, whereas, populations with conformist social learners achieves higher average population reward in environments with high uncertainty.