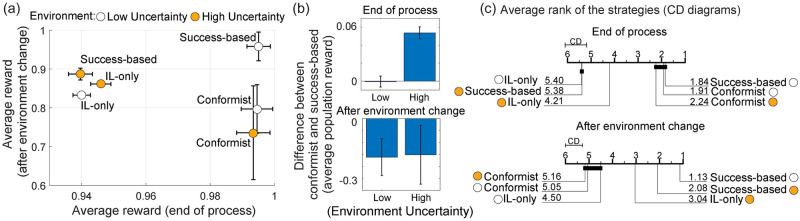
Fig 2. Performance of individual and success-based and conformist learning strategies.
The success-based strategy shows the best performance in environments with low uncertainty, however, it suffers when there is uncertainty in the environment. On the other hand, the conformist strategy achieves similar performance independent of the environment uncertainty. (a) The average rewards achieved by the strategies after an environment change vs. at the end of the processes in environments with high and low uncertainty. (b) The difference in the performance of conformist vs success-based strategies. After an environment change, the performance achieved by the success-based strategy is higher in low and high uncertainty environments, whereas, at the end of the processes, they achieve similar results only in low uncertainty environment. On the other hand, in high uncertainty environment the performance of the conformist strategy is higher. Finally (c) provides the Critical Difference diagrams (CD) shows the average ranks of the the strategies (given by decimal numerals in each line that represent a strategy) based on their performance after an environment change and at the end of the processes. Lower ranks demonstrate better performance in terms of average population reward achieved by the strategies. The strategies are linked (via bold thick lines) if their average ranks are not statistically significant based on the post-hoc Nemenyi test at α = 0.05 [48, 49].