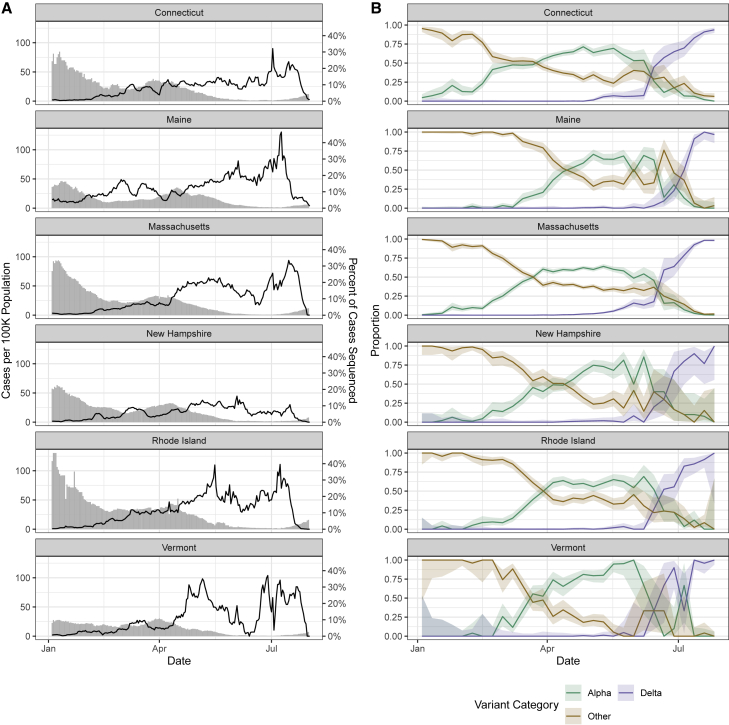
Figure 1.
SARS-CoV-2 sequencing coverage and variant frequency tracking
(A) Confirmed cases per 100,000 population (bars) and percentage of cases sequenced (lines) by state (7 day rolling average), January to August 2021. The variability in percentage of cases sequenced represents changing sample availability and suitability for sequencing. The drop in percentage sequenced at the end of August does not reflect real decreases in sequencing coverage but instead (1) the 1 to 3 week delays between sample collection and sequence availability and (2) how the data are plotted using 7 day rolling averages.
(B) Weekly proportion of sequenced genomes belonging to each variant category with 95% confidence intervals, January to August 2021. A breakdown of the number of genomes (n = 33,408) by state and lineage is included in Tables S1–S3.