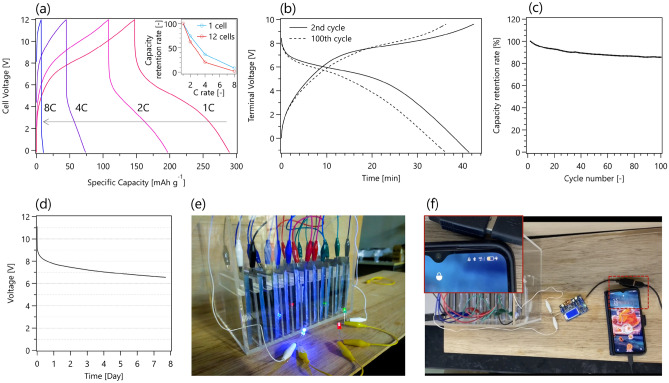
Figure 3.
(a) Charge and discharge profiles of a high-voltage cell (twelve single cells connected in series) with different C rates (1 C, 2 C, 4 C, and 8 C). The inset shows the capacity retention rates of a single cell and a high-voltage cell based on the capacities at a 1 C rate. (b) Charge and discharge profiles of a high-voltage cell at a 1 C rate for the 2nd and 100th cycle. (c) The capacity retention rate of a high-voltage cell for 100 cycles at a 1 C rate. (d) Transition of open-circuit voltage of a fully charged high-voltage cell for more than 7 days. (e) A picture of a high-voltage aqueous supercapacitor illuminating three different LED bulbs (red, green, and blue) connected in series, which requires at least 6.9 V. (f) A smartphone is charged by a high-voltage aqueous supercapacitor.